
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- Securing GROW with SAP Landscape
Technology Blogs by SAP
Learn how to extend and personalize SAP applications. Follow the SAP technology blog for insights into SAP BTP, ABAP, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP HANA, and more.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Advisor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-20-2023
6:36 AM
(Jana Subramanian serves as APJ Principal Cybersecurity Advisor for Cloud Security and has been recognized as a Fellow of Information Privacy (FIP) by the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP). As part of his responsibilities, Jana helps with strategic customer engagements related to topics such as cybersecurity, data privacy, multi-cloud security integration architecture, contractual assurance, audit, and compliance.)
Introduction
SAP has introduced GROW with SAP in March 2023 as a means of supporting mid-sized businesses on their journey to Cloud ERP. The GROW with SAP package encompasses several key components, including cloud ERP solution - SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition , SAP Business Technology Platform with certain CPEA credits, pre-configured baseline and packaged activation services, SAP Build Services, and expert user support through SAP Community among others. This offering helps customers to manage business operation with an enhanced cloud-based system, delivering security, flexibility, and predictable cost.
GROW with SAP bundle provides comprehensive security and ensures that customer core applications and data are protected through secure operations. In this blog, we will delve into the security features of the cloud-based ERP solution provided by GROW with SAP bundle offering and how it enables businesses of various sizes to protect their core valuable assets and data.
Shared Security Responsibility
SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition is offered as public SaaS. SAP takes responsibility for ensuring the security of the SaaS platform architecture through advanced multi-tenant logical separation, security patching, managing backup and restoration, as well as securing infrastructure elements such as operating systems, networking, and applications. Additionally, SAP handles cloud (Hyperscaler) account management, operational security monitoring, incident management, personal data breach notifications, hardening and patching operating systems, application and providing solution support. Adherence to SLAs and contractual assurance is maintained through SAP Service Level Agreements, SAP Data Processing Agreements, General Terms and Conditions and SAP support policy. Customers are responsible for managing application layer security, user authentication, authorization, and secure integration to third-party systems and data privacy settings. The table below provides insight into the shared security responsibilities between SAP and the customer for key security topics.
For more details, please refer to the reference documentation for SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition.
Customer Access to SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition
Secure Customer Data Segregation
In the SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition each customer's environment is segregated using Security Group. Security Groups provide a mechanism for controlling access and communication between different resources in the cloud. This isolation ensures that customers' applications and data are not exposed to other customers' environments. Every tenant has their own ABAP application servers that operate on distinct SAP HANA tenant databases. The SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition relies on multi-tenant database containers (MDC) feature of SAP HANA database allowing multiple isolated databases, referred to as "Tenant DB”. Tenant DB refers to independent databases that are part of a single SAP HANA system database. These databases store all the application data and configuration that are specific to each tenant. Therefore, each SAP HANA Tenant DB has its own set of tables, users, and security policies, and can be managed independently of other Tenant DB on the same system.
Customer security group allows system communication between various environment of the same customer. Within a customer's environment, there are three system landscape: Development (D), Testing (T), and Production (P). The customer security group enables secure communication between these systems, ensuring that only authorized users and resources within the same customer's environment can access and interact with the data and processes in these systems.
Integrated Secure Landscape
A secure connectivity from SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition and SAP Business Technology Platform can be established via several methods that includes support for standard OData services in SAP S/4HANA cloud that can be consumed by applications running on SAP BTP, Integration Suite in SAP BTP to integrate SAP S/4HANA Cloud with other services and applications on SAP BTP by creating integration flows that define how data is exchanged between the systems.
Additionally customer’s expose SAP S/4HANA Cloud services as APIs and consume them in your applications on SAP BTP. The secure connectivity can be established between SAP S/4HANA Cloud and SAP BTP leveraging security and authentication mechanisms available such as OAuth 2.0, SAML 2.0, and Client certificates. For example, SAP S/4HANA Cloud uses OAuth 2.0 for authentication and authorization. This ensures that only authorized users and applications can access data in SAP BTP.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition subscription contains embedded SAP Analytics Cloud and is automatically deployed and configured during tenant provisioning. However, this is limited to only live connection to S/4HANA Cloud tenant.
Encryption Controls:
By default, SAP manages encryption key for data at rest encryption keys for SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition. To manage the encryption keys, two Secure Stores in the File System (SSFS) are used. The Instance SSFS stores various encryption root keys (data volume, log volume, backup), while the System PKI SSFS stores system-internal root certificates for secure internal communication. The contents of both SSFSs are protected by SSFS Master Keys, which are generated during installation. There is an option for customers to use Customer-Controlled Encryption Key integration, You can refer to the documentation for details.
API Security:
Customers should follow best practice approach to security settings under their responsibility. SAP BTP provide API Security in API Management. The SAP S/4HANA cloud provides Business user Change API, Security Audit Log API, Business Role Change API, OAuth 2.0, SAML2.0, Cross Origin Resource Sharing security. Besides, customer should ensure establishing strong authentication methods for business users, such as multi-factor authentication and single sign-on. Additionally, it is crucial to define and enforce appropriate authorization levels based on users' roles, securely configure, and manage trusted certificates for secure communication channels and implement read access logging to monitor and audit data access for potential security breaches or unauthorized activities.
Data Protection and Privacy
While SAP, as a data processor, is committed to protecting data through its Data Processing Agreement and Technical and Organisational Measures, SAP S/4HANA cloud application offers built-in security features and specific data protection functions that customers can easily customize to their needs to meet their data privacy compliance. These functions include consent management, security audit logs, read access logs, blocking, and deletion of personal data.
For more details in Data Protection and Privacy features available with SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition, please refer to this documentation.
Additional References
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is paramount for safeguarding critical assets in all businesses, regardless of their size and scale. The GROW with SAP bundle addresses this need by providing a holistic approach to cybersecurity and data privacy requirements. This comprehensive offering not only ensures the protection of a company's core assets but also affords flexibility, seamless integration, and the ability to extend and modernize their core ERP digitally. Thus, as mid-sized businesses adapt to the changing digital landscape, adopting the GROW with SAP bundle can help them enhance their cybersecurity posture and compliance measures.
Disclaimer:
© 2023 SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. See Legal Notice on www.sap.com/legal-notice for use terms, disclaimers, disclosures, or restrictions related to SAP Materials for general audiences.
Introduction
SAP has introduced GROW with SAP in March 2023 as a means of supporting mid-sized businesses on their journey to Cloud ERP. The GROW with SAP package encompasses several key components, including cloud ERP solution - SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition , SAP Business Technology Platform with certain CPEA credits, pre-configured baseline and packaged activation services, SAP Build Services, and expert user support through SAP Community among others. This offering helps customers to manage business operation with an enhanced cloud-based system, delivering security, flexibility, and predictable cost.
GROW with SAP bundle provides comprehensive security and ensures that customer core applications and data are protected through secure operations. In this blog, we will delve into the security features of the cloud-based ERP solution provided by GROW with SAP bundle offering and how it enables businesses of various sizes to protect their core valuable assets and data.

Figure 1: SAP Secure Cloud Operations
Shared Security Responsibility
SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition is offered as public SaaS. SAP takes responsibility for ensuring the security of the SaaS platform architecture through advanced multi-tenant logical separation, security patching, managing backup and restoration, as well as securing infrastructure elements such as operating systems, networking, and applications. Additionally, SAP handles cloud (Hyperscaler) account management, operational security monitoring, incident management, personal data breach notifications, hardening and patching operating systems, application and providing solution support. Adherence to SLAs and contractual assurance is maintained through SAP Service Level Agreements, SAP Data Processing Agreements, General Terms and Conditions and SAP support policy. Customers are responsible for managing application layer security, user authentication, authorization, and secure integration to third-party systems and data privacy settings. The table below provides insight into the shared security responsibilities between SAP and the customer for key security topics.
| S.No | Security Theme | SAP Responsibility | Customer Responsibility |
| 1 | Business/Customer User Authentication |
|
|
| 2 | Authorization |
|
|
| 3 | Network Security |
|
|
| 4 | Security Patch Management |
|
|
| 5 | Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) |
|
|
| 6 | Logging and Monitoring |
|
|
| 7 | Encryption |
|
|
| 8 | Backup and restore |
|
|
| 9 | Retention and Deletion |
|
|
| 10 | Virus Scans on the Uploaded Content |
|
|
| 11 | Secure by Design and Secure by Default |
|
|
| 12 | Connectivity |
|
|
| 13 | Disaster Recovery |
|
|
For more details, please refer to the reference documentation for SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition.
Customer Access to SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition
- The SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition is hosted in SAP Converged Data Center, Azure, and Google Cloud at various global locations. In the SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Public Edition and SAP BTP, business users access the application via a standard browser, providing a seamless user experience across all devices and Fiori applications through the Fiori Launchpad.
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud uses a load balancer and a web dispatcher. The incoming request is directed to the load balancer. The load balancer distributes incoming network traffic across shared web dispatcher cluster. Each customer accesses their system through a unique, customer-specific URL, with communication managed by the SAP Web Dispatcher's Reverse Proxy component. The web dispatcher is responsible for routing incoming requests from the load balancer to the customer specific application (ABAP)
- Standard users authenticate using SAML 2.0 assertions (SSO) through SAP Cloud Identity, ensuring secure access to the system. It handles authentication, ensuring that end users can securely access the system.
- At the backend, the SAP HANA database powers the system, providing optimized access through Core Data Services (CDS) views. Both the SAP S/4HANA ABAP and SAP HANA components are managed by SAP, ensuring a reliable and secure environment for users.

Figure 2: Customer Access to SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition
Secure Customer Data Segregation
In the SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition each customer's environment is segregated using Security Group. Security Groups provide a mechanism for controlling access and communication between different resources in the cloud. This isolation ensures that customers' applications and data are not exposed to other customers' environments. Every tenant has their own ABAP application servers that operate on distinct SAP HANA tenant databases. The SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition relies on multi-tenant database containers (MDC) feature of SAP HANA database allowing multiple isolated databases, referred to as "Tenant DB”. Tenant DB refers to independent databases that are part of a single SAP HANA system database. These databases store all the application data and configuration that are specific to each tenant. Therefore, each SAP HANA Tenant DB has its own set of tables, users, and security policies, and can be managed independently of other Tenant DB on the same system.
Customer security group allows system communication between various environment of the same customer. Within a customer's environment, there are three system landscape: Development (D), Testing (T), and Production (P). The customer security group enables secure communication between these systems, ensuring that only authorized users and resources within the same customer's environment can access and interact with the data and processes in these systems.
Integrated Secure Landscape
A secure connectivity from SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition and SAP Business Technology Platform can be established via several methods that includes support for standard OData services in SAP S/4HANA cloud that can be consumed by applications running on SAP BTP, Integration Suite in SAP BTP to integrate SAP S/4HANA Cloud with other services and applications on SAP BTP by creating integration flows that define how data is exchanged between the systems.
Additionally customer’s expose SAP S/4HANA Cloud services as APIs and consume them in your applications on SAP BTP. The secure connectivity can be established between SAP S/4HANA Cloud and SAP BTP leveraging security and authentication mechanisms available such as OAuth 2.0, SAML 2.0, and Client certificates. For example, SAP S/4HANA Cloud uses OAuth 2.0 for authentication and authorization. This ensures that only authorized users and applications can access data in SAP BTP.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition subscription contains embedded SAP Analytics Cloud and is automatically deployed and configured during tenant provisioning. However, this is limited to only live connection to S/4HANA Cloud tenant.

Figure 3: Secure Integrated Landscape
Encryption Controls:
By default, SAP manages encryption key for data at rest encryption keys for SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition. To manage the encryption keys, two Secure Stores in the File System (SSFS) are used. The Instance SSFS stores various encryption root keys (data volume, log volume, backup), while the System PKI SSFS stores system-internal root certificates for secure internal communication. The contents of both SSFSs are protected by SSFS Master Keys, which are generated during installation. There is an option for customers to use Customer-Controlled Encryption Key integration, You can refer to the documentation for details.
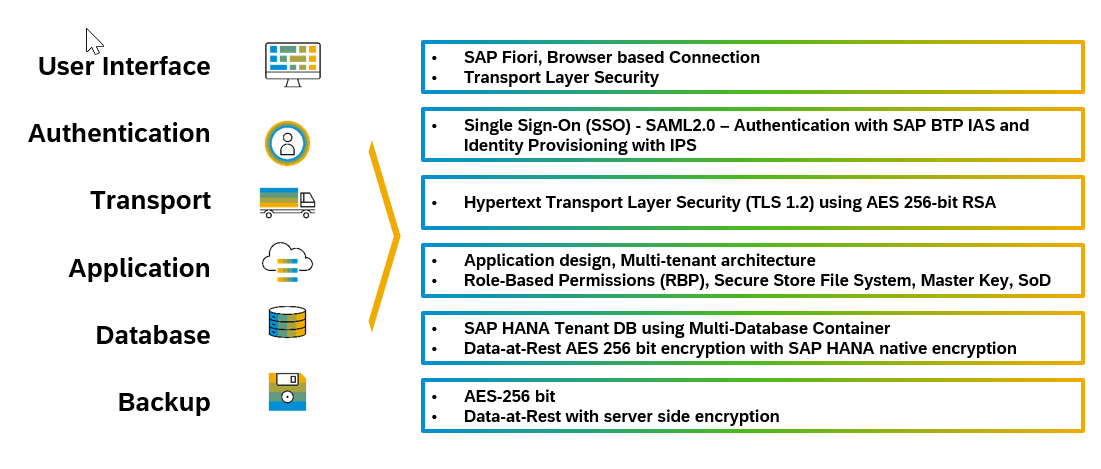
Figure 4: Data Protection and Encryption Stack
API Security:
Customers should follow best practice approach to security settings under their responsibility. SAP BTP provide API Security in API Management. The SAP S/4HANA cloud provides Business user Change API, Security Audit Log API, Business Role Change API, OAuth 2.0, SAML2.0, Cross Origin Resource Sharing security. Besides, customer should ensure establishing strong authentication methods for business users, such as multi-factor authentication and single sign-on. Additionally, it is crucial to define and enforce appropriate authorization levels based on users' roles, securely configure, and manage trusted certificates for secure communication channels and implement read access logging to monitor and audit data access for potential security breaches or unauthorized activities.

Figure 5: API Security
Data Protection and Privacy
While SAP, as a data processor, is committed to protecting data through its Data Processing Agreement and Technical and Organisational Measures, SAP S/4HANA cloud application offers built-in security features and specific data protection functions that customers can easily customize to their needs to meet their data privacy compliance. These functions include consent management, security audit logs, read access logs, blocking, and deletion of personal data.

Figure 6: Data Privacy in SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition
For more details in Data Protection and Privacy features available with SAP S/4HANA cloud, public edition, please refer to this documentation.
Additional References
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is paramount for safeguarding critical assets in all businesses, regardless of their size and scale. The GROW with SAP bundle addresses this need by providing a holistic approach to cybersecurity and data privacy requirements. This comprehensive offering not only ensures the protection of a company's core assets but also affords flexibility, seamless integration, and the ability to extend and modernize their core ERP digitally. Thus, as mid-sized businesses adapt to the changing digital landscape, adopting the GROW with SAP bundle can help them enhance their cybersecurity posture and compliance measures.
Disclaimer:
© 2023 SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved. See Legal Notice on www.sap.com/legal-notice for use terms, disclaimers, disclosures, or restrictions related to SAP Materials for general audiences.
Labels:
2 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,658 -
Business Trends
112 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
74 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
177 -
Expert Insights
348 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
GraphQL
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
780 -
Life at SAP
14 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,575 -
Product Updates
391 -
Replication Flow
1 -
REST API
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,871 -
Technology Updates
483 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
Related Content
- SAP Datasphere – Security Concept in Technology Blogs by Members
- How to Connect a Fieldglass System to SAP Start in Technology Blogs by SAP
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP BTP - Blog 7 Interview in Technology Blogs by SAP
- cds view not visible in sac in qual environnement but Ok in dev in Technology Q&A
- RingFencing & DeCoupling S/4HANA with Enterprise Blockchain and SAP BTP - Ultimate Cyber Security 🚀 in Technology Blogs by Members
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 14 | |
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 10 | |
| 9 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 |