
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- ILM Store Configuration
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
With the ILM Store, you have access to SAP's own store for data retention. This enables the storing of archive files using Retention Management for SAP Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) in an SAP database such as SAP IQ or SAP HANA and stay within the SAP environment.
The storage media supported currently are:
- File System (or within the same System DB)
- HANA
- IQ
- HADOOP
This blog covers how to set up a basic ILM Store and use the same system DB as store or a secondary DB like IQ or HANA.
This document is just a quick setup checklist. Use the Installation & Config. Guide ILM Store document available in the below location for the complete document.
[[ https://help.sap.com/viewer/product/SAP_INFORMATION_LIFECYCLE_MANAGEMENT/7.0/en-US ]]
Also refer the help documentation for more details. https://help.sap.com/saphelp_nw74/helpdata/en/27/017835919640619f07e7fc3e6ef599/frameset.htm
You can follow the below steps to configure the ILM Store in an NW 750 SP02 and higher systems.
1. Prerequisites needed
To be able to use the ILM Store, the prerequisite is to switch on the ILM Store (ILM_STOR) business function and the Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) business function.
2. SICF Service for ILM Store
A service for ILM Store should be created and activated in transaction SICF.
- Start transaction SICF and create a new service under node ILM and enter the following values.
Service name: ZILM_STOR (for example)

- On the Logon Data tab, enter a user who has the authorization to access the ILM Store.
This user should have the following authorizations
-Authorization object SILMSTOR with activity ACTVT = 16 (Execute)
-Authorization object S_DATASET with the following values to this user so that the file system can be used to temporarily store the data:
File Name: *
Program: CL_ILM_STOR_DATASET===========CP and RILM_STOR_PUT_WORKER
The following activities added to the authorization object:
06 = Delete
33 = Read
34 = Write
-Authorization object S_DEVELOP for temporary table creation
OBJTYPE = 'TABL'
ACTVT = 07 and 40
-Authorization Object S_CTS_ADMI : CTS_ADMFCT = 'TABL'
-Authorization Object S_CTS_SADM: CTS_ADMFCT = 'TABL'
- On the Handler List tab, enter the handler class (CL_ILM_STOR_WD_REQUEST_HANDLER).

- Activate the service
3. Create RFC Destination
Go to transaction SM59. Create a new HTTP connection to the external server (type G).

Maintain the target host and service number corresponding to your system.
The path prefix that you define on the Settings tab represents the connection between the destination and the ICF node. So give the service path which you have defined using SICF in previous step.
4. Commands for using File System
You need three commands for working with the file system:
- ILM_STOR_DIR
- ILM_STOR_MKDIR
- ILM_STOR_DIR_FILES
You can use the transaction External Operating System Commands (SM69) to execute these commands. Refer the ILM Store configuration guide (mentioned in point 1) for more information on this.
Command name: ILM_STOR_MKDIR
Operating system:
1.WINDOWS NT:
Operating system command: cmd /C mkdir
Parameters for operating system command: <empty>
2.UNIX:
Operating system command: mkdir
Parameters for operating system command: -p
3.[x] Additional parameters allowed
4.Check module: FM_ILM_STOR_MKDIR_CHECK
Command name: ILM_STOR_DIR
Operating system:
1.WINDOWS NT:
Operating system command: cmd /C dir
Parameters for operating system command: /AD /L /B
2.UNIX:
Operating system command: ls
Parameters for operating system command: -d
3.[x] Additional parameters allowed
4.Check module: FM_ILM_STOR_DIR_CHECK.
Command name: ILM_STOR_DIR_FILES
Operating system:
1.WINDOWS NT:
Operating system command: cmd /C dir
Parameters for operating system command: /AD /L /B
2.UNIX:
Operating system command: find
Parameters for operating system command: <empty>
3.[x] Additional parameters allowed
4.Check module: FM_ILM_STOR_DIR_CHECK.
If you cannot create these commands with the names as above, create it in your dedicated namespace.
You can run the report RILM_STOR_TEST_SM69 to create these Z commands for the UNIX and Windows NT systems.
Please note : If you are using this report to create the commands, then do after maintaining the origin in step 5. In this report you have to give your origin in the selection.
5. Configuration required for IQ and HANA
For IQ and HANA, there is a secondary database connection required.
In DBCO, this connection needs to be maintained.
The user entered in the DBCON entry needs to have the have the rights CREATE TABLE, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE.
For IQ set variable ENABLE_LOB_VARIABLES into the public space:
set option PUBLIC.ENABLE_LOB_VARIABLES = ON. Also the UDA license needs to be generated for using BLOBs.
Use report ADBC_TEST_CONNECTION to check for any connection issues.
6. Store Origin Customization
- Go to Transaction ILM_STOR_ADM_CUST and click on “Create”.
- Fill the required entries:

- Click on “Add Operational Origin”.

- Fill in required details and save.
DB Connection = DEFAULT( for same system DB) or
Secondary DB connection name (in case of IQ and HANA DB)

- Maintain Operational Customizing in transaction ILM_STOR_OPR_CUST.
Enter Client maintained in Administrative Origin client.


Select the namespace SYSTEM and maintain the operating system commands if you have created in your namespace, else you can keep the standard one itself. (Alternatively, you can use the report RILM_STOR_TEST_SM69 for the Z commands as mentioned in section 5.) This is required for the default set up and not needed in case of IQ and HANA DB.
In case, you want to use the File System as storage media, change the entries as below in SM30 for table TILM_STOR_CUS.
| Origin | Namespace | Property | Value |
| adk | DB | DBCON.TILM_STOR_BLOB | SAP_CONN_DEF |
| adk | DB | CONSYS.SAP_CONN_DEF | SAP_SYS_FILE |
7. Maintain entries in TILMSTOR_CF
In transaction SM30, Table – TILMSTOR_CF -> New Entries.

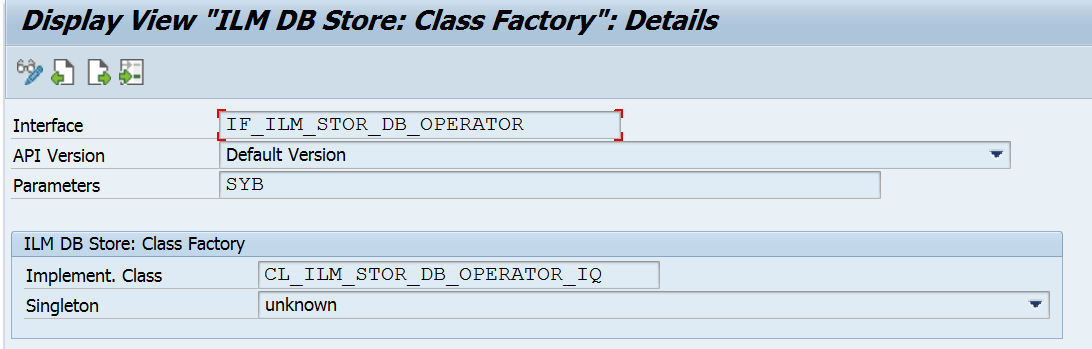

8. Maintain entries in TILM_STOR_O_ROUT
Make an entry in TILM_STOR_O_ROUT table as below.
Go to SM30. Table – TILM_STOR_O_ROUT -> New Entries.
SAP System ID : <System ID>
Client:<Client>
Data Source: <Your operational origin>

9. Activate SRS for ILM Stores
To use Storage and Retention Service (SRS) for managing ILM stores, you need to activate SRS in the application system.
To activate SRS, the following options are available:
- Activate the SRS that runs locally in the application system.
- Activate the SRS that runs on a separate (remote) system. For this option, you need an HTTP connection between the relevant systems.
Please use the below help link to set this up.
https://help.sap.com/saphelp_pobuilder10/helpdata/en/49/1ccd91d83d4a7f846788f36bd01013/content.htm?n...
10. Maintain Store in ILMSTOREADM
After you have created the destination, you can enter it in the list of stores that are available for the SRS. Do the below for this.
- To do so, start transaction ILMSTOREADM.
- Enter the following values:
ILM Store: An identifying name for the store
Description: Descriptive text
HTTP connection: The previously created RFC destination

11. Testing the Store
TEST REPORT
Report RILM_STOR_TEST_PF_SINGLE can be used to test the store functionality.
For this, the test origin archeb is used.
In table TILM_STOR_CUS (use transaction SM30), create the entries for archeb similar to how you have maintained for your origin.
In the report selection, provide the RFC destination and execute.
Use report RILM_STOR_TEST_CLEAR to clear previous test entries.
The logs can be seen through SLG1 -> Object = ILM_STOR.
HEALTH CHECK REPORTS
Run the health check reports to check your configurations.
Check the errors and warnings and check if action need to be taken.
- RILM_STOR_TEST_HC_SERVER - You use the Health Check for Server Configuration report to validate the configuration settings and the viability of the ILM Store. The report identifies missing configuration settings, which can cause communication errors.
- RILM_STOR_TEST_HC_CLIENT - If you also want to check for archiving client also, use the report RILM_STOR_TEST_HC_CLIENT to validate the configuration settings of the archiving client that communicates with the ILM Store.
Enter the following ILM Store connection parameters:
- Target Host – the name of the application server where the ILM Store is installed and configured
- Port – the port number through which the two systems communicate using the HTTP protocol
- ICF Service Path – the service that processes the requests from the client
- System ID – the ID of the system to which the client connects
- Client – the client number of the system to which the client connects
All values for the input fields are available in the results of the Health Check for Server Configuration (RILM_STOR_TEST_HC_SERVER) report.
Select one of the following execution targets:
- Archiving Client (Local Storage and Retention Service (SRS)) – You make this selection if the execution target is an archiving client. In this option, the SRS is set to local on the archiving client. The report verifies the location of the SRS. If the location is local, the Health Check for Client Configuration report checks the SRS configuration directly on the archiving client system.
If the SRS is accessed remotely, execute the report for the client using the External SRS Client option.
- External SRS Client – You make this selection if the SRS is set up as a remote service. The Health Check for Client Configuration report is executed on the external SRS system. The system skips the checks that are only relevant for the archiving client.
STORING ARCHIVE FILES
After this to test the archive files stored, create rules in IRMPOL for the required ILM Objects and give the store as the one created in point 10. Now run the archiving process and store the files and check if successful.
Following these steps, you should be able to successfully store your files into the ILM Store. In case of any issues, raise an incident to BC-ILM-STO.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Information Lifecycle Management,
- NW ABAP Data Archiving
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,658 -
Business Trends
102 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
69 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
177 -
Expert Insights
322 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
GraphQL
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
780 -
Life at SAP
13 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,576 -
Product Updates
367 -
Replication Flow
1 -
REST API
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,873 -
Technology Updates
454 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
- How to Deploy Package /SALM/CHARM_REPACK_MS to Managed System? in Technology Q&A
- revamped SAP First Guidance Collection in Technology Blogs by Members
- SAP Cloud ALM - Granular Authorization to Scopes in Technology Q&A
- Monitoring Apps on Kyma in Technology Q&A
- How to setup SAP Build process automation action project and cap multi tenant application? in Technology Q&A
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 23 | |
| 11 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 |