
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- First Time Right with Trusted Business Partner Dat...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) is designed to effectively manage, consolidate, and improve the quality of business partner data. It integrates seamlessly with CDQ, providing access to reliable data from various trusted data sources such as open data, trade registers, and commercial data providers. This integration leads to quicker processes and improved data quality for creating and maintaining customer and vendor data
I am Kai Hüner, responsible for the SAP-endorsed app CDQ First Time Right at CDQ AG. In this blog post, I will explain the benefits of the integration of CDQ as a provider of trusted business partner data in SAP MDG with real-world examples. I will keep this blog post updated with new features to ensure it always reflects the latest information about the capabilities of this integration.
Topics covered
- What is trusted business partner data good for?
- Architecture: Integration of CDQ in SAP MDG
- Highlight: Lookup trusted business partner data
- Highlight: Seamless integration of tax numbers and identifications
- Highlight: Even more identifiers with the Golden Record
- Highlight: Uniform categorization of legal forms
- Key takeaway
Update log
- 2024-01-31: Feature highlight Even more identifiers with the Golden Record added.
What is trusted business partner data good for?
Trusted business partner data is pivotal for any organization, serving as a foundation upon which key operational and strategic decisions are made. Beyond the accuracy and timeliness of the data itself, understanding its provenance -- or where it comes from -- is equally crucial. Data provenance allows businesses to assess the reliability of their data, ensuring that they are basing decisions on information derived from credible and authoritative sources.
In the realm of business partner data, where multiple external data types like open data, commercial data, shared data, and web data intersect, provenance information is the key to trust and reliability. For a more detailed exploration of this concept and its implications, see my blog post Value Creation with Trusted Business Partner Data.
Architecture: Integration of CDQ in SAP MDG
In SAP MDG, access to external business partner data is enabled by the Data Provider Integration (DPI) feature, part of the Central Governance capability. In the 2023 release, SAP introduced the cloud-ready mode for MDG, based on ABAP Cloud. Since the Business Partner Data domain was the starting point for this development, and DPI was one of the first features in this mode, it is now available in all major MDG editions -- SAP MDG on S/4HANA (aka "MDG on-premise"), private cloud edition, and (public) cloud edition. SAP provides a uniform user experience across these various editions. This consistency is made possible through Fiori apps that offer the same features regardless of the MDG edition being used (see the Highlight sections below).
If you are interested in a free-of-charge test and demo setup, see my blog post Hands-on with Free Tiers: CDQ Trusted Business Partner Data in SAP Master Data Governance.
Architecture: SAP Master Data Governance on S/4HANA
The following solution diagram shows you how trusted business partner data from CDQ is integrated in SAP MDG on S/4HANA. CDQ provides access to all its connected external data sources through a REST API. This involves two main endpoints: Lookup Business Partners to search and find potential matches, and Fetch Business Partners to get detailed data for the match you choose.
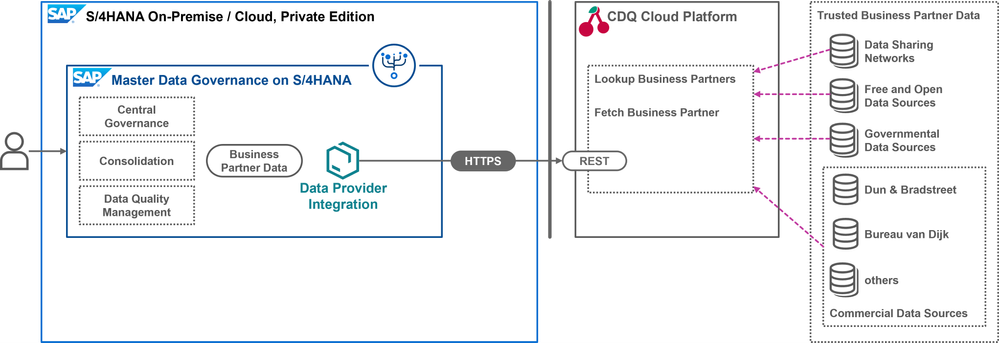
If you are interested in a detailed walk-through on how to set up and configure the CDQ integration in an SAP MDG on S/HANA environment, see my blog post Trusted Business Partner Data in SAP Master Data Governance on S/4HANA, On-Premise and Private Cloud.
Architecture: SAP Master Data Governance, cloud edition
Trusted business partner data from CDQ can also be utilized in public cloud environments through SAP MDG, cloud edition. By incorporating integration solutions like SAP Master Data Integration (MDI) or SAP Cloud Connector, this architecture offers even more options, such as for federated MDG landscapes or integrating with SAP Business Suite environments.
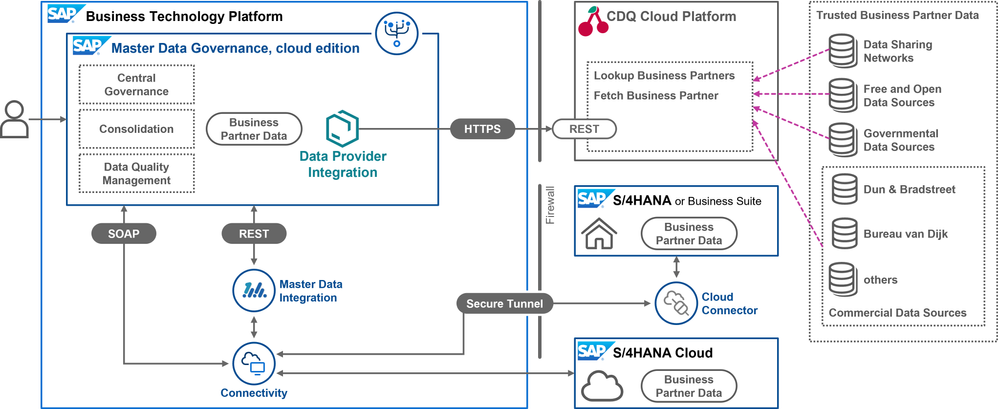
If you are interested in a detailed walk-through on how to set up and configure the CDQ integration in an SAP MDG, cloud edition, environment, see my blog post Trusted Business Partner Data in SAP Master Data Governance, cloud edition.
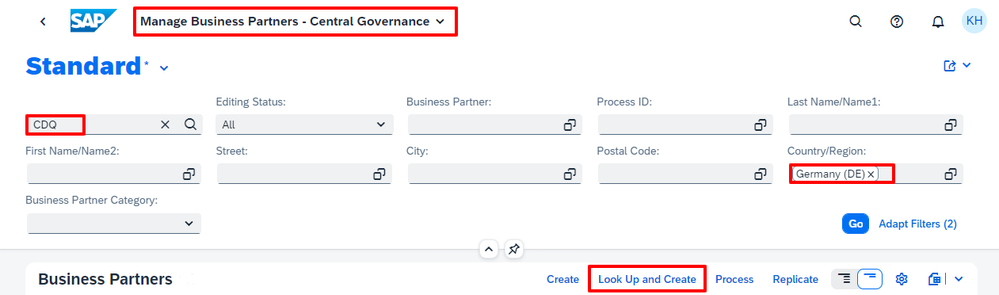
Highlight: Lookup trusted business partner data
And here we go: The first and most fundamental feature highlight of trusted data from CDQ in SAP MDG! In my Fiori Launchpad, I go to the Manage Business Partners app and search for CDQ in Germany (DE). With Look Up and Create, I get matches with business partner data from various trusted data sources!
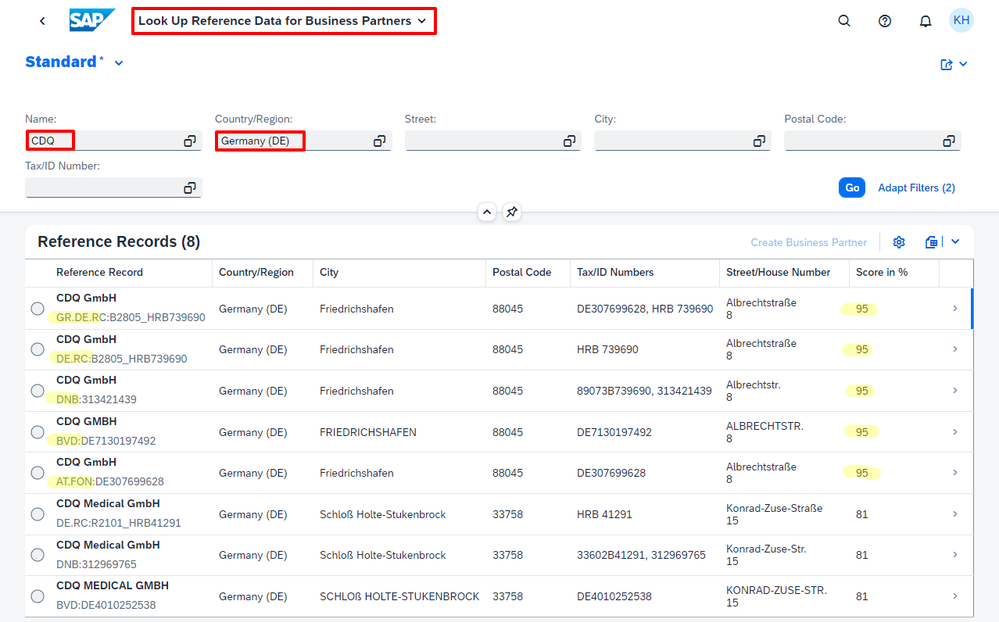
The figure shows the search result for CDQ in Germany (DE) with five matching reference records. Under the company name of each item, the prefix of the record ID indicates the data source for the corresponding record. For instance, DE.RC stands for the German Register of Commerce, DNB represents Dun and Bradstreet, BVD denotes Bureau von Dijk, and AT.FON refers to Austrian FinanzOnline. The first item is marked with GR, Golden Record, a consolidated version of the data from all other records using a prioritization logic.
Highlight: Seamless integration of tax numbers and identifications
One of the key highlights is that the identifiers of various data sources are mapped to SAP's standard tax categories and identification types. These mappings can be customized to comply with corporate standards, but they also work out-of-the-box for most used identifiers. In the example, the ID of the German Register of Commerce is mapped to BUP002, which is the SAP identification type for business register numbers. And additional information such as the responsible institution is mapped to the corresponding SAP field.
In SAP's data model (One Domain Model, ODM), there are two key types of identifiers for business partners: Identifications and Tax Numbers. Both are vital components of various business processes, requiring precise semantic mapping to external data. While SAP MDG allows for customized code lists, I strongly recommend sticking to default settings, especially for tax numbers due to their deep integration in tax-related processes.
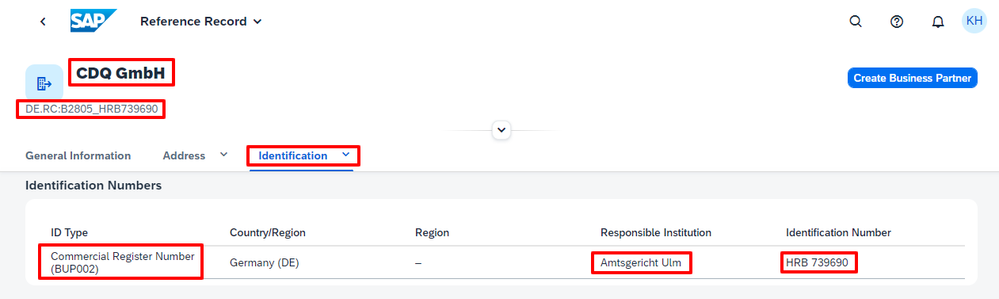
For example, if you find a matching business partner with a value-added tax (VAT) number in an external data source, this information will be automatically mapped to the corresponding SAP tax number type code. To demonstrate this, I perform a lookup for CDQ in Germany (DE).
In the detailed view, under the Identifications section, the European VAT number is accurately mapped to DE1. Additionally, the German trade register identification number is mapped to BUP002. This also includes essential details like the name of the register court and the region, which are crucial for uniqueness in Germany. All of this is automatically mapped, eliminating the need for manual research to find the correct types and codes. How cool is that!
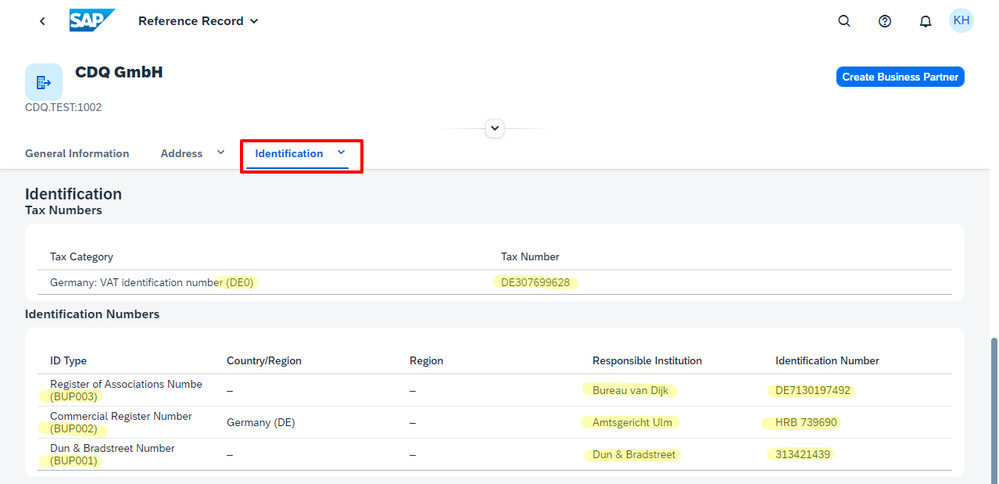
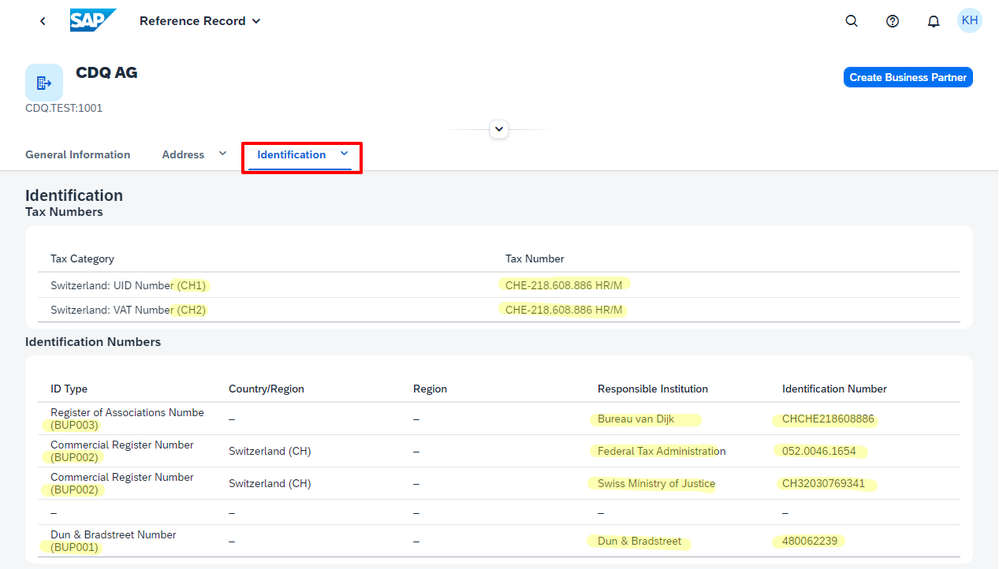
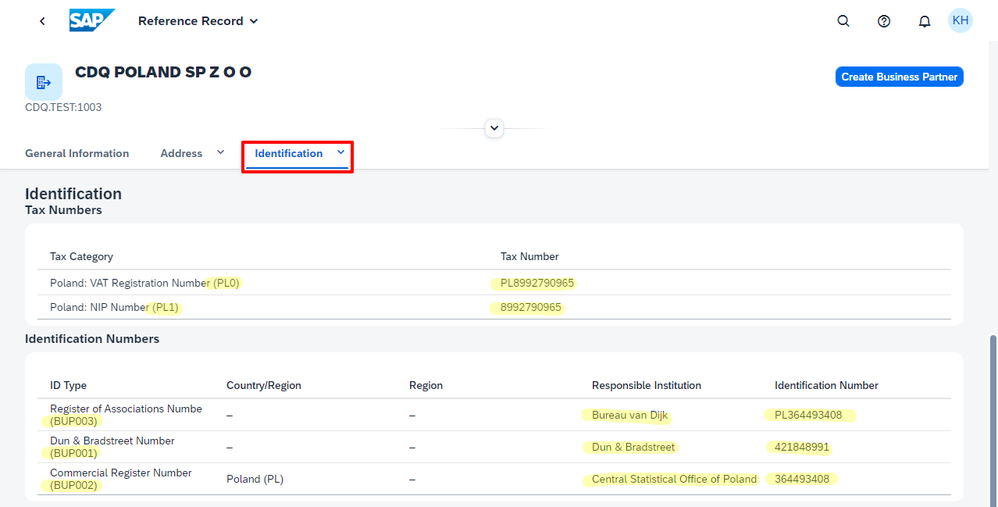
Finding matches for CDQ in Switzerland (CH), and Poland (PL), serves as more evidence of how valuable this automated mapping is. In these countries too, you will notice that the tax number and identification types are automatically mapped to the right SAP type codes. This shows how the system can handle different international standards with ease, making your work more efficient.
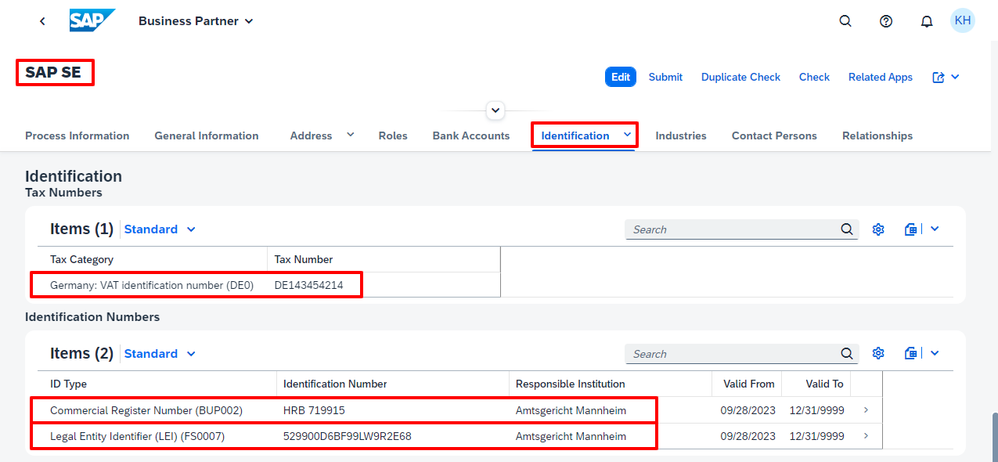
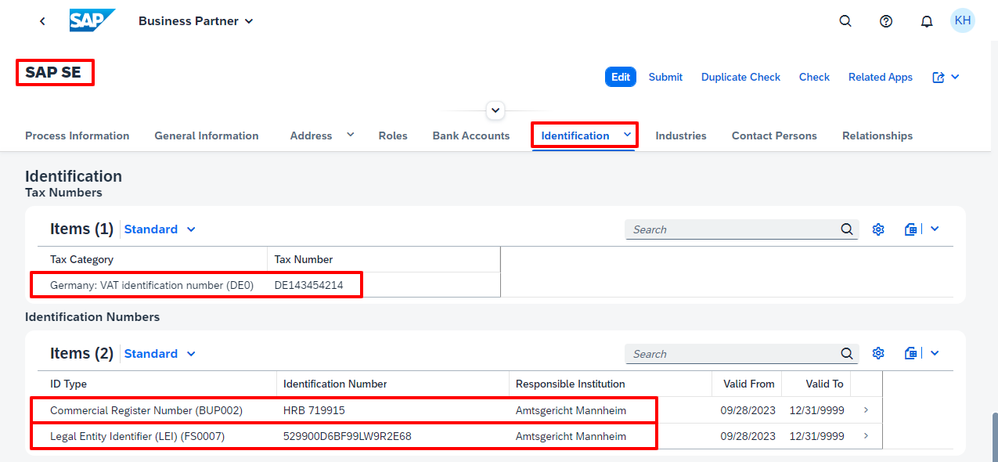
For major corporations like SAP, the scope of identifiers extends further, encompassing options like the Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) or Peppol directory identifiers for e-invoicing. While the free tier dataset offers just a glimpse through exemplary records, a search for SAP SE in Germany (DE), illustrates the significant advantages of integrating trusted data from CDQ. All essential business identifiers are automatically mapped to the data model of your SAP MDG.
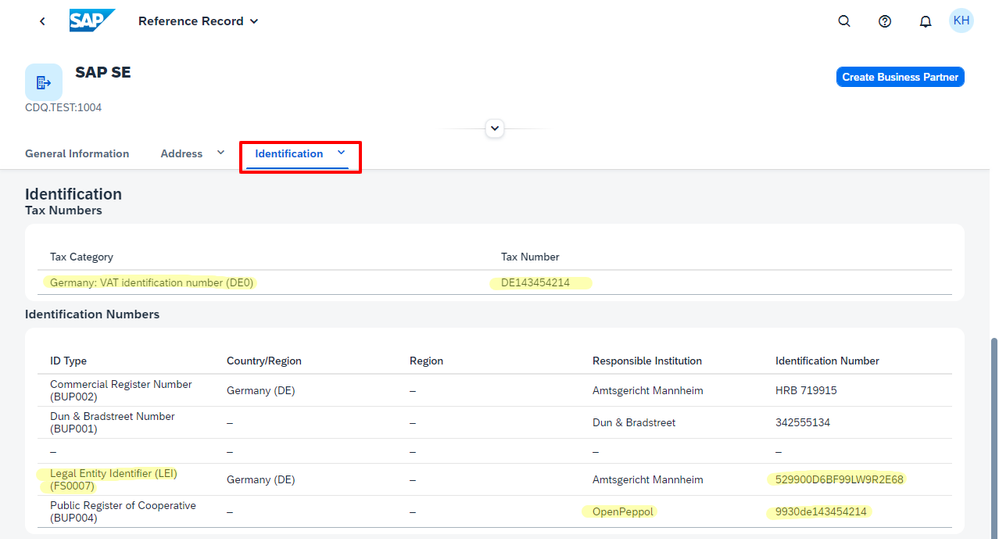
Highlight: Even more identifiers with the Golden Record
As the search result for CDQ in Germany (DE) shows, multiple relevant reference records for a particular business partner may appear across various data sources. The Golden Record feature addresses this issue by consolidating information from multiple sources into one consistent record, with a prioritization of data sources that is customizable and country-specific. As shown in the figure below, the European VAT number is included with information from the German Register of Commerce and mapped to the SAP tax category DE0.
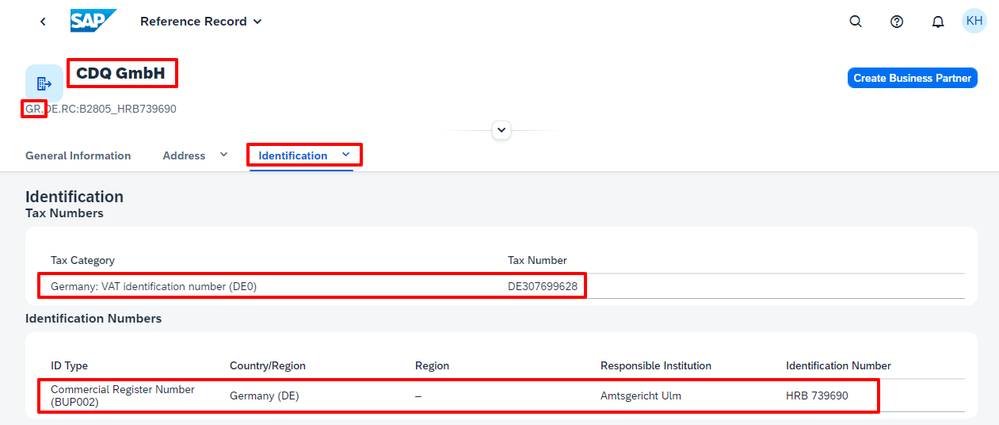
Integrated data sources are not limited to German or European authorities but include a variety of sources from around the world. For example, the Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) in the following example is just one of many IDs that can be accessed. Trusted data sources from various US state registers, Brazil, Australia, and other countries are also available.
Highlight: Uniform categorization of legal forms
Understanding a business partner's legal form is crucial for global risk management. Legal forms are defined differently in various countries, adding complexity to this matter. Some data sources offer structured information on legal forms, while others include it informally as part of the name, and some do not offer this information at all. SAP ODM addresses this by providing a legal form attribute within a business partner's organizational details. However, this attribute has limitations such as a two-character code and various namespace restrictions.
To tackle these challenges, we at CDQ have defined about 90 legal form categories. These categories link to the various legal forms and their abbreviations across countries.
In SAP MDG, the system allows only a two-digit code and a unified abbreviation for the legal form category. However, even with these limitations, you gain a standardized view of your business partners' legal forms on a global scale.
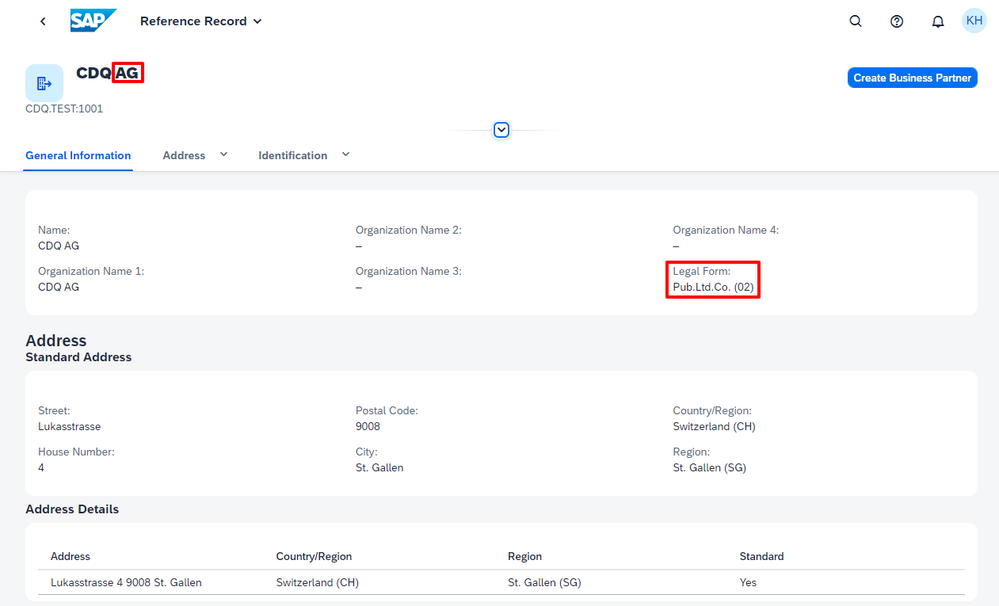
Back in my SAP MDG system, after searching for CDQ in Switzerland (CH), I click on the matching result to view more details. Here, the legal form is displayed as Pub.Ltd.Co., with an associated SAP code of 02. This code universally represents public limited companies, capturing both Aktiengesellschaft and Société Anonyme in Switzerland, as well as PLC in Great Britain.
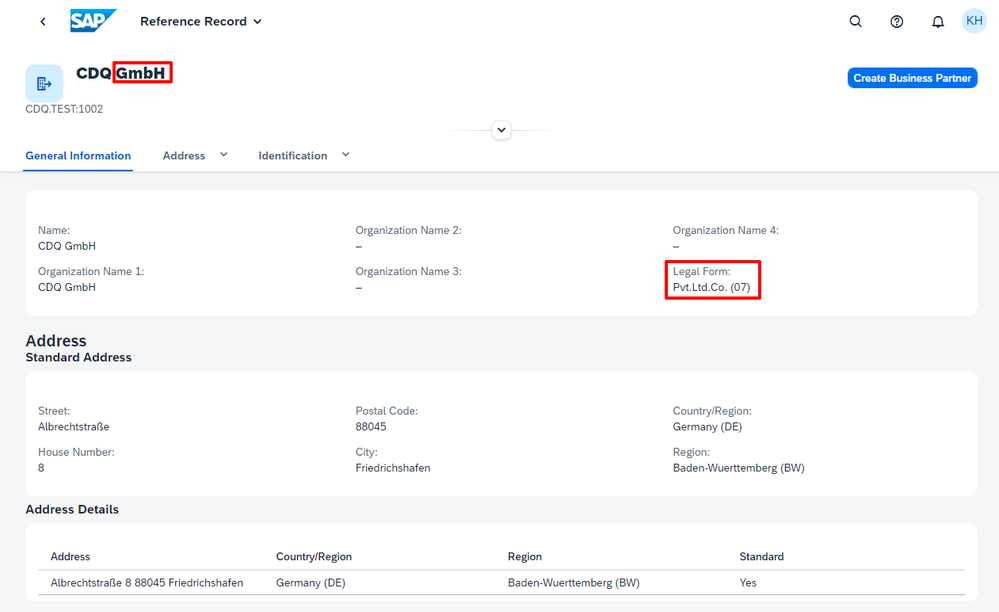
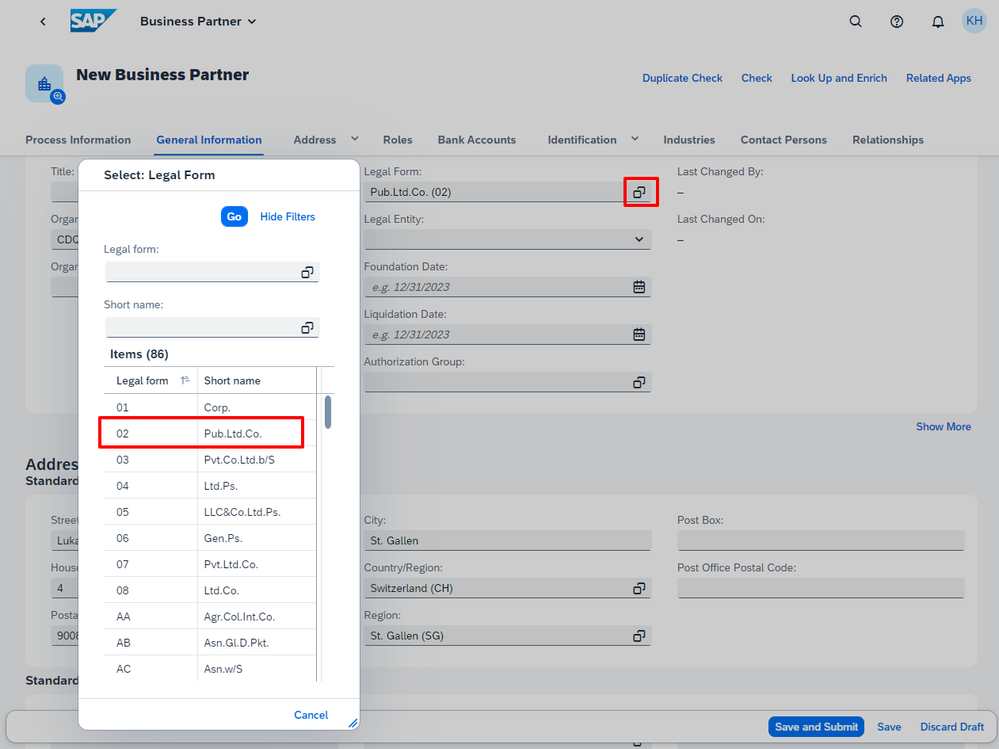
When I initiate the Create Business Partner process, a value help dialog for legal forms becomes accessible, displaying all the legal forms I had uploaded as business configurations from the content pack.
Next, I compare this with match record details for CDQ in Germany (DE) and Poland (PL). I notice that the German legal form AG, and the Polish legal form SP Z O O both fall under the same legal form category Pvt.Limited.Co. (private limited companies), represented by the SAP code 07. The uniform categorization simplifies the process of understanding and comparing business partners across different countries.
Key takeaways
SAP MDG provides a robust framework that ensures data integrity, paving the way for businesses to make informed decisions grounded in accurate and current data. One of its significant advantages is the capability to incorporate data from external sources, broadening the scope and reliability of the data available.
The synergy between SAP MDG and external data providers, exemplified by the CDQ integration, elevates the potential benefits businesses can achieve from their data. It complements the role of SAP MDG in creating a trustworthy data governance environment. Our collaboration with SAP MDG is a prime example of this integration. At CDQ, we have pioneered the Golden Record concept, a method that consolidates data from multiple sources into a single, dependable record.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP S/4HANA business partner,
- SAP Master Data Governance,
- SAP Business Technology Platform
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
3 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
abapGit
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
Advanced formula
1 -
AEM
1 -
AI
8 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
API security
1 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
Azure API Center
1 -
Azure API Management
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
Bank Communication Management
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
13 -
BTP AI Launchpad
1 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Fabric
1 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
BW4HANA
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
4 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
2 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
4 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Flow
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Dataframe
1 -
Datasphere
3 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Defender
1 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ESLint
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Exploits
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
first-guidance
1 -
Flask
1 -
FTC
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
gCTS
1 -
GenAI hub
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
9 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
Hana Vector Engine
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
Infuse AI
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
iot
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
Loading Indicator
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
4 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multilayer Perceptron
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Myself Transformation
1 -
Neo
1 -
Neural Networks
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
3 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
Partner Built Foundation Model
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Prettier
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
6 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
python library - Document information extraction service
1 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
4 -
S4HANA Cloud
1 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
9 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP API Management
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
22 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
6 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Generative AI
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP BTPEA
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
3 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HANA PAL
1 -
SAP HANA Vector
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP LAGGING AND SLOW
1 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Master Data
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
2 -
SAP PAL
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapfirstguidance
1 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
SAPIQ
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
5 -
schedule
1 -
Script Operator
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
Self Transformation
1 -
Self-Transformation
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
Slow loading
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
15 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Threats
2 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transformation Flow
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
3 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Vectorization
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
2 -
VSCode extenions
1 -
Vulnerabilities
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- More About Cloud-Ready Mode in SAP Master Data Governance in Technology Blogs by SAP
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP Business Technology Platform - Blog 6 in Technology Blogs by SAP
- User centricity opens the door to a successful SAP S/4HANA Cloud implementation in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Introducing the New E-learning ‘Clean Core with SAP Business Technology Platform’ in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Vectorize your data for Infuse AI in to Business using Hana Vector and Generative AI in Technology Blogs by Members
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 10 | |
| 8 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |