
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by SAP
- Advanced WIP reporting in S/4HANA Cloud Public Edi...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Co-Authored by Gabi Hoffmann and Stefan Walz
Welcome to this blog, in which we will show the new capabilities in Event-Based Revenue Recognition for advanced WIP (Work-in-Progress) reporting. The screenshots are taken from an SAP S/4HANA Cloud CE2402 system; the described functionality is only available in public cloud.
This functionality is based on the professional service tailored customer project scenario using time & expense billing.
We will start in this blog with a functional overview. Then we will show an end-to end process in the system based on the professional service tailored customer project scenario. For time and expense billing scenario there are many functionalities provided by the Manage Project Billing app, which are reflected in EBRR. We will close with insights into the EBRR configuration.
Motivation and functional scope
Motivation
The WIP on customer projects with the T&E billing method needs to be reported and justified to internal and external stakeholders such as auditors. First the WIP must be distinguished by (travel)expenses and hours (consultants time confirmation). For the WIP built by time confirmation it is important to know the underlying number of billable hours. The reporting must be possible too for previous periods – like the last year-end close.
Solution approach
The prerequisite to provide such enhanced reporting – even for previous periods - requires a solution based on journal entries posted by EBRR and supplementary information to be added.
With the new rev rec method, we have updated the existing ACDOCA fields Quantity and product (ACDOCA-MATNR) for the EBRR journal entries. This ensures, that the complete WIP can be explained by billed product, and therefore by time – including hours - and expenses portions.
This functionality is provided by the new revenue recognition key SPTMWP, which uses a new T&E revenue recognition method and a new assignment rule. This method only works in public cloud for professional service customer projects with T&E contract items.
The new method enhances the existing reporting capabilities for WIP:
- Drilldown by market segment fields like product sold, customer or sales order – please check in figure 1.
- Information about employee performing the service and Cost Analysis Resource – only available for T&E contract items and target revenue method.
Further information about the professional service customer project processes is available here:
https://blogs.sap.com/2018/06/26/financial-accounting-for-customer-projects-in-sap-s4hana-cloud-part...
Features of the new revenue recognition key/method
- The EBRR journal entries are enhanced by the hours and the billed product
Important: only hours are reflected, not other Unit of Measures. - Write-off and CAP postings can now be determined by journal entry item attributes, stored in the field SLA Line item type.
- To enhance transparency, we have reduced the journal entry items for the CAP postings.
Since we write all the information to the general ledger, it is available for the current and each previous period. This means for example, that the WIP of the last fiscal year end close can be analyzed at any time.
Note to SLA Line item type (subledger specific line item type)
With the SLA item type, in General Ledger we distinguish further the kind of journal entry posting. For example, event-based revenue recognition: The business transaction type is defined as TBRR. But to distinguish the kind of journal entry item further, we use the SLA Line item type: accrued revenues/WIP, revenue adjustment, deferred revenues and now CAP and write off. Or we distinguish customer downpayment on projects: https://community.sap.com/t5/enterprise-resource-planning-blogs-by-sap/down-payment-4-customer-proje...
Remark to WIP Details app
This app can also be used to analyze the current WIP for T&E contract items in great detail. You can also determine the WIP aging. For this, in addition to the posting date, the service rendered date is available.
However, the report is not intended for declaring the WIP for a point in time in the past. - e.g. at the year-end or last month-end close. Examples of restrictions:
- There is only one currency conversion date for a project in foreign currency.
- If repricing has taken place in the meantime, the open quantities will be valued with the new price.
- If all open billable items have been invoiced or written off in the meantime, the billing element is no longer selected.
System walkthrough – new WIP reporting for customer projects
We will now show an end-to end process in a CE2402 system for a professional service project, which is billed based on confirmed time and expenses.
We will post three time confirmations of different employees:
- One senior consultant posting with activity type T002 and mapped to a bill product T002.
- Two platinum consultants posting activity type T003, mapped to bill product T003. One employee is a cross company resource.
Additionally, we post travel expenses to the project, the expense G/L account is mapped to bill product E001.
With the Manage Project Billing app we will bill one hour and write off one hour.
We will show, how these business transactions are reflected in the General ledger journal entries and which WIP analysis is now available
First, we post a time confirmation for Platinum Consulting – activity type T003 - of 6 hours, which leads to the following journal entries
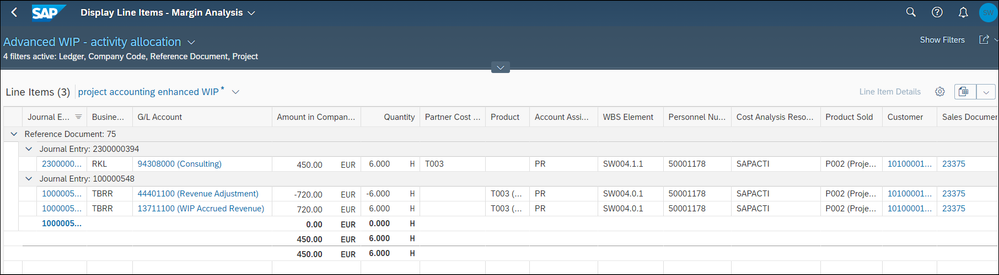
The second journal entry reflects the matching EBRR journal entry. The realized revenue and therefore also the WIP is calculated by simulating time & expense-based project billing.
The activity type T003 is mapped to the bill product T003. The amount to be billed is calculated by SD pricing based on the customer and the billed material T003. Here we get 120€ per hour T003, which leads to the billable amount and realized revenue of 720€.
The billed product is stored in the revenue recognition journal entry items as well as the billable hours of 6.
As before we store the performing employee, Personnel number, and the Cost Analysis Resource. SAPACTI means activity allocation of an intracompany employee.
The EBRR journal entry items are account assigned to the WBS billing element, Account Assignment Type = PR, and thus the market segment attribution is active. We derive the assigned sales order, 23375. From the sales order we get the customer, 10100001, and from the item the product sold P002. In case of T&E billing, P002 is not the product, which is billed, it describes the delivered service – like S/4HANA implementation consulting project.
More about the CO account assignment and attribution functionality in S/4HANA is available here: https://community.sap.com/t5/enterprise-resource-planning-blogs-by-sap/co-account-assignment-and-att...
In the next step we post travel expenses on the customer project – using the Post General Journal Entry app.

The second journal entry reflects the matching EBRR journal entry. As for the time confirmation the realized revenue and therefore also the WIP is calculated by simulating time & expense-based project billing.
The G/L account 61003000 “Travel Expense – Hotel” is mapped to the bill product E001. The amount to be billed is defined in project billing: for bill material E001 the posted cost amount is billed to the customer 1:1. So, we get the same amount to be billed and therefore realized revenue as for the costs.
The billed product E001 is stored in the revenue recognition journal entry.
As before we store the performing employee, Personnel number, and the Cost Analysis Resource. SAPEXPI means expense posting of an intracompany employee.
Additionally, we post two time confirmations:
5h of an intercompany employee – Resource SAPACTCC – activity cross company
and 5 hours of an intracompany senior consultant – Resource SAPACTI
We now analyze the activated WIP on the customer project with the Display Line Items – Margin Analysis app (the apps Display line items - General Ledger or Display Line Items – Cost Accounting can be taken too)
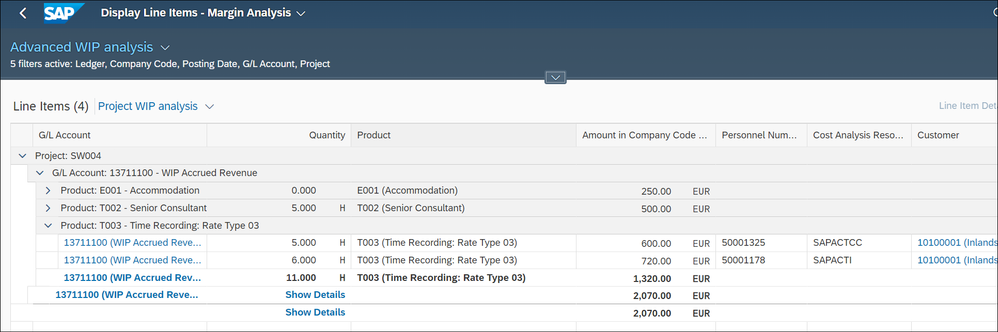
The complete WIP of 2.070€ can be explained by billed product.
The WIP contains expenses of 250€
And time of 1820€, which consists of:
- Billed product T002, Senior consulting, of 500€, confirmed 5h
- Billed product T003, Platinum consulting, of 1320€, confirmed 11h
Thus, our WIP contains 16h - the hours we confirmed before.
Now let us start billing preparation with the Manage Project Billing app. The app allows the user – typically the project manager - to create customer invoices based on the journal entries posted. For each wbs billing element, all time confirmation and expense postings are displayed. the project manager can then decide on the basis of the individual confirmations what is to be billed, what to postpone or written off. These decisions have direct impact on EBRR.

We get an overview of all confirmations – the 16 hours and the posted expenses.
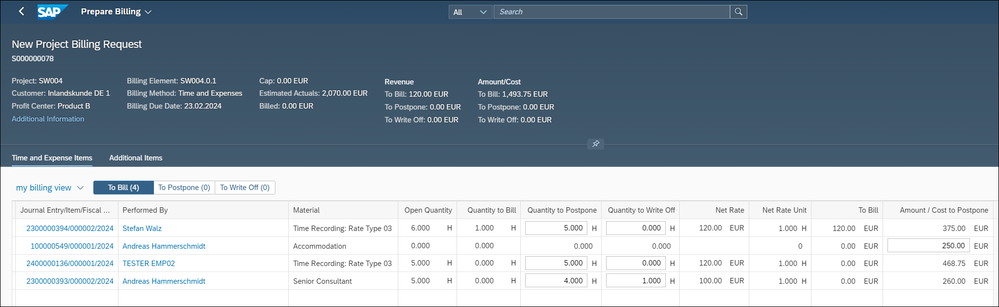
The first line, item is a platinum time confirmation of 6 hours: we postpone 5h and bill one hour.
The second item is the travel expense of 250€, which we postpone.
The third line item is the intercompany platinum time confirmation of 5h, which we postpone.
The fourth line item is the time confirmation of 5h of the senior consultant, employee Andreas Hammerschmidt: we postpone 4 hours and write off 1h.
By pushing submit:
- we get the billing document request created.
- We get an EBRR document created, which reduces the WIP and realized revenue for the 1h written off.
- The postponed Billable Items are still in WIP.
By submitting the Prepare Billing app we get an EBRR document created automatically to reflect the off hour.
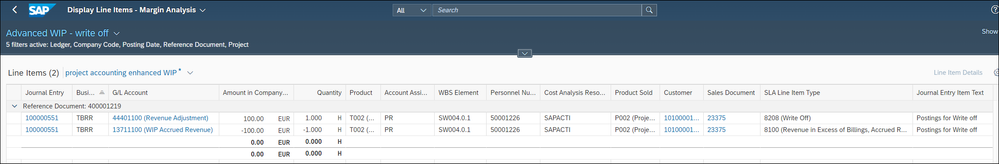
Additionally, we update in both journal entry items the hours: the billable quantity and thus the WIP quantity is reduced by 1 hour.
To allow reporting on the written off hours we use an own new SLA type 8208 for write off for the revenue adjustment journal entry item.
With an additional step we create the billing document, which we show in figure 7.
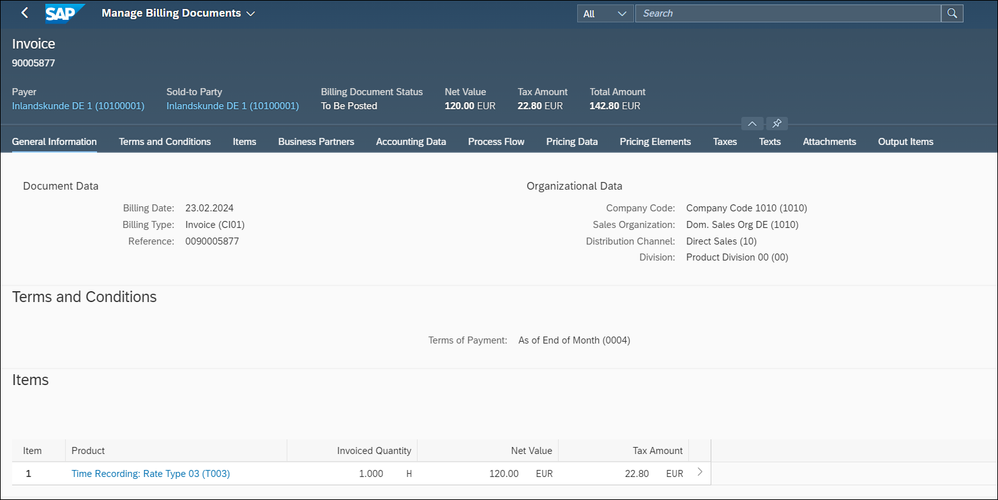
We post the billing document to accounting and analyze it:
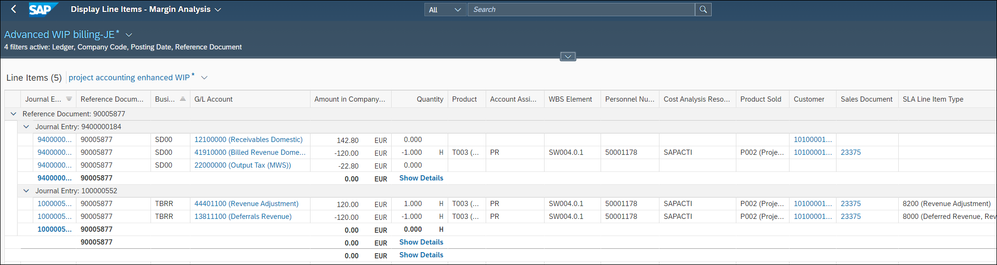
The second journal entry is the matching EBRR document, in which we now write the billed product T003 and the quantity of 1h with the new EBRR method.
Other attributes are provided as explained before.
As next step we start an EBRR period-end calculation with the Event-Based Revenue Recognition – Projects app. We select our Billing element SW004.0.1 and start Revalue. In the pop up we select Simulate and get the results in figure 10.
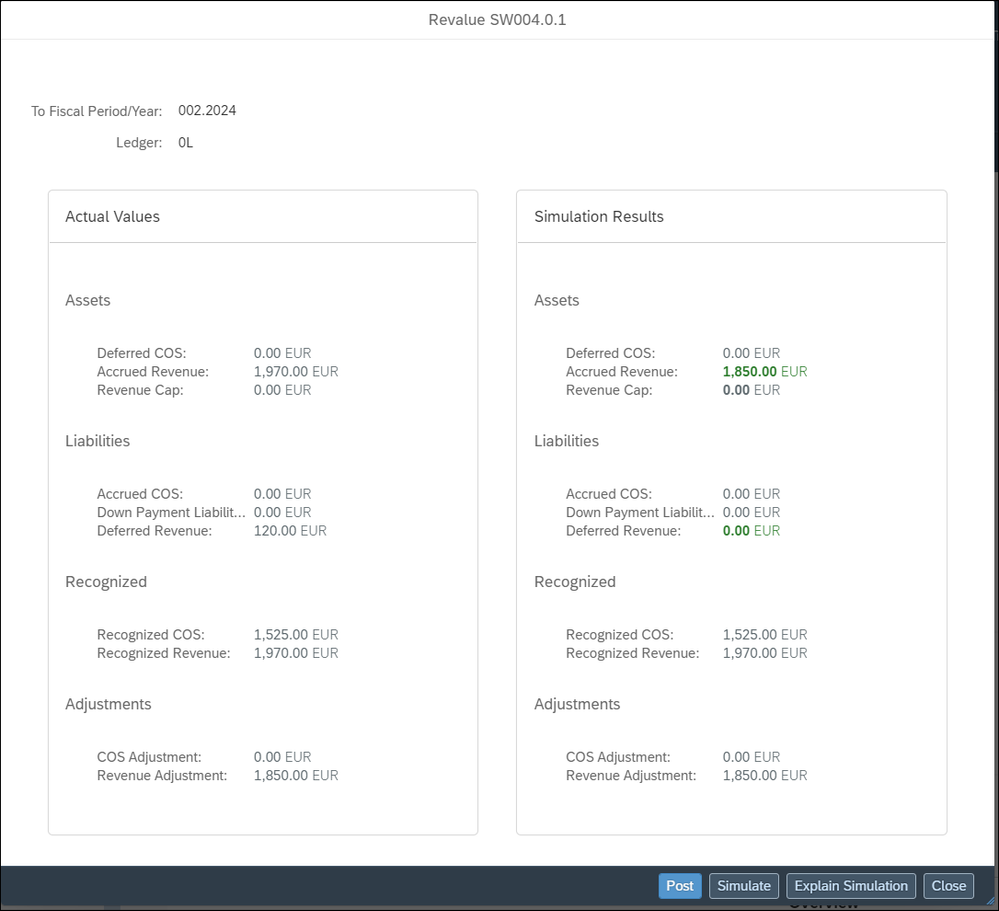
The created EBRR document we analyze in Figure11.

Now let’s have a final look on the WIP reports. We will focus on the new reporting capabilities bill product, quantity and new SLA Line item type for analysis of the write off.
First, we analyze again the WIP in figure 12
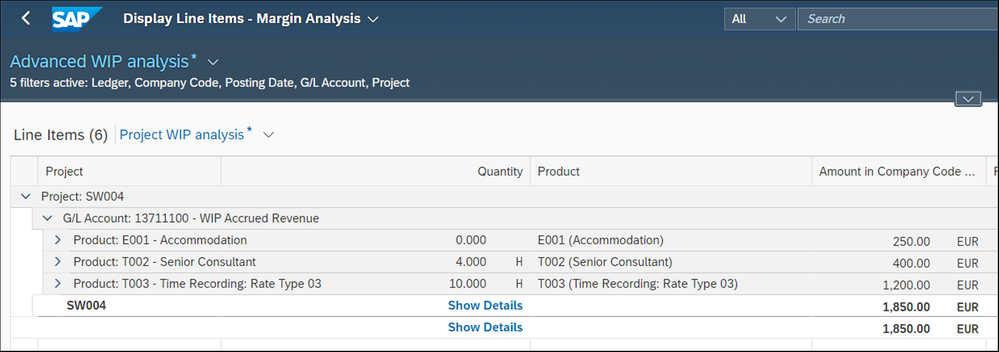
There are still 14 hours in WIP.
Now we want to trace the hours handled within the project. We select all relevant postings for the project.
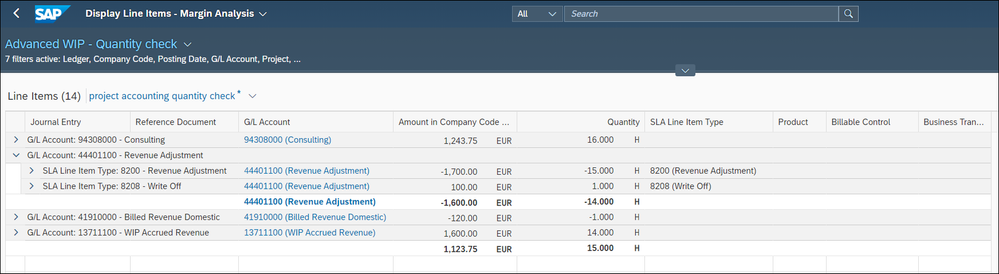
Confirmed hours (16h) = Billed hours(1h) + write off (1h) + WIP (14h)
The confirmed/input hours we get in first line with the consultant’s time confirmations – G/L account 94308000.
The billed hours we get through the billing journal entry item on the project – G/L account 41910000.
The written off hours we detect by the SLA type 8208.
The WIP quantities we get with the G/L account 13711100.
Not covered in our example are the non billable hours. They can be analyzed via the journal entry item field "billable control".
Now let’s check the WIP with the Display Project WIP Details app.
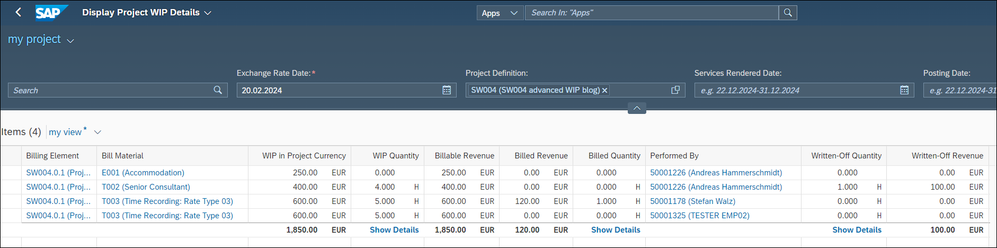
But with this new revenue recognition functionality the shown reporting based on Journal entries in Figure 12 and Figure 13 would work for all cases.
Let’s have a look, how special features in the professional service requirements are covered.
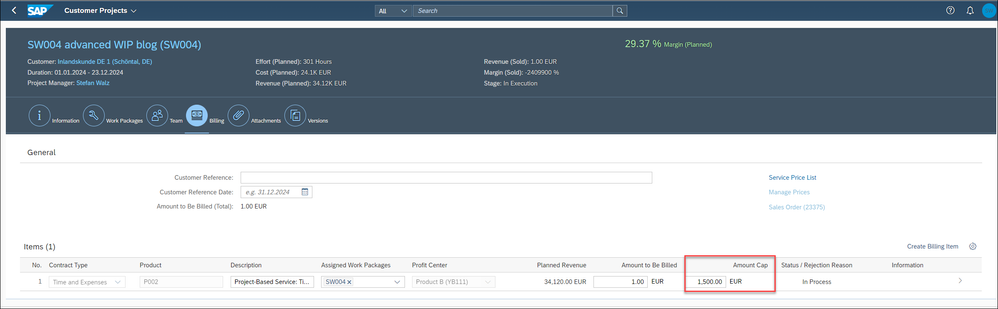
CAP Handling
Although the T&E billing method is selected for the WBS billing element, it is possible that a maximum amount has initially been agreed with the customer that cannot be exceeded. For this purpose, a CAP value can be stored for the WBS billing element.
Then we start again EBRR period-end calculation with the Event-Based Revenue Recognition – Projects app. We select our Billing element SW004.0.1 and start Revalue. In the pop up we select Simulate and get the results in figure 16.
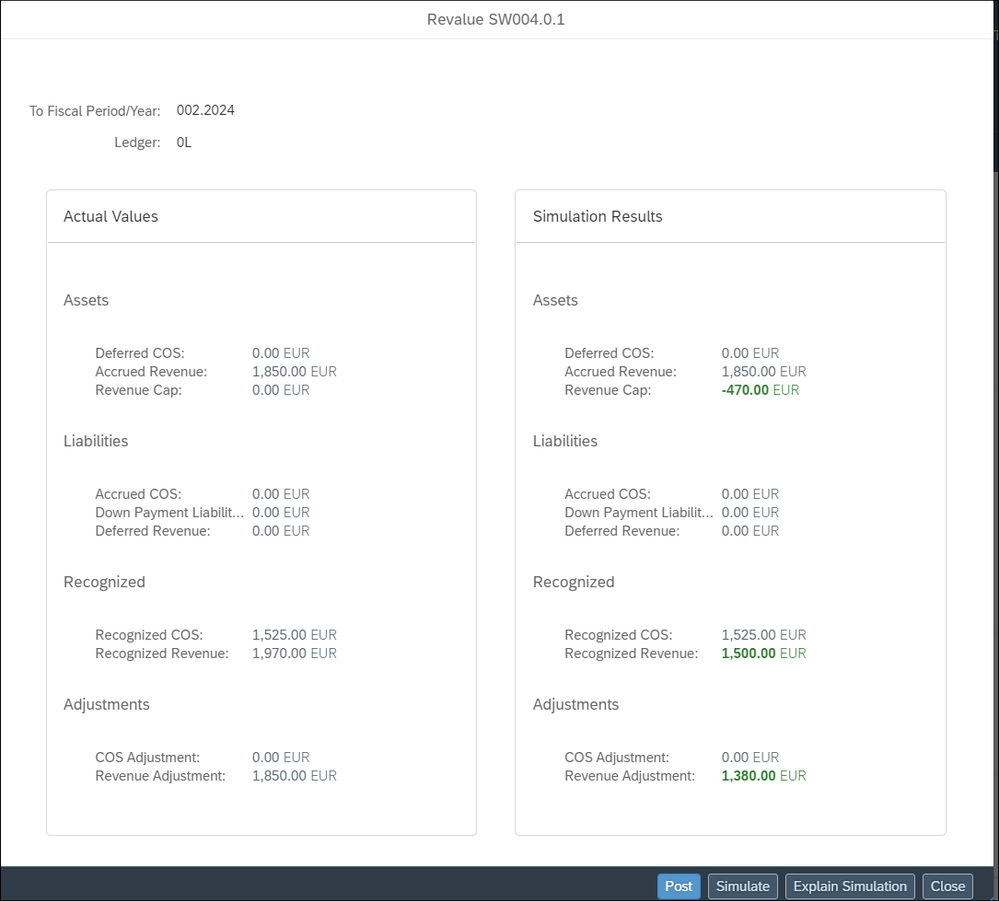
The created EBRR document we analyze in Figure17.
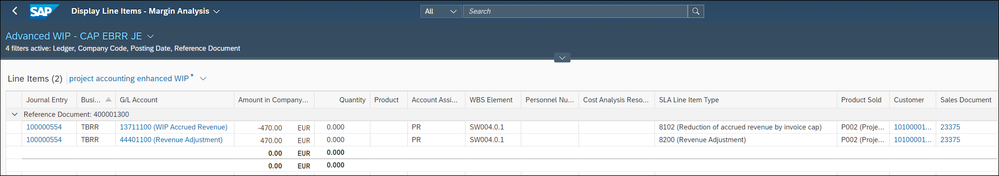
We simplified the posting as the information is only relevant for G/L. This reduction is temporary and will we replaced by a later decision of the project manager to bill or to write off. These postings will then adjust the additional attributes – as shown above.
This simplified CAP handling, and the new SLA type is controlled by a new usage in EBRR config – please check next chapter figure 22.
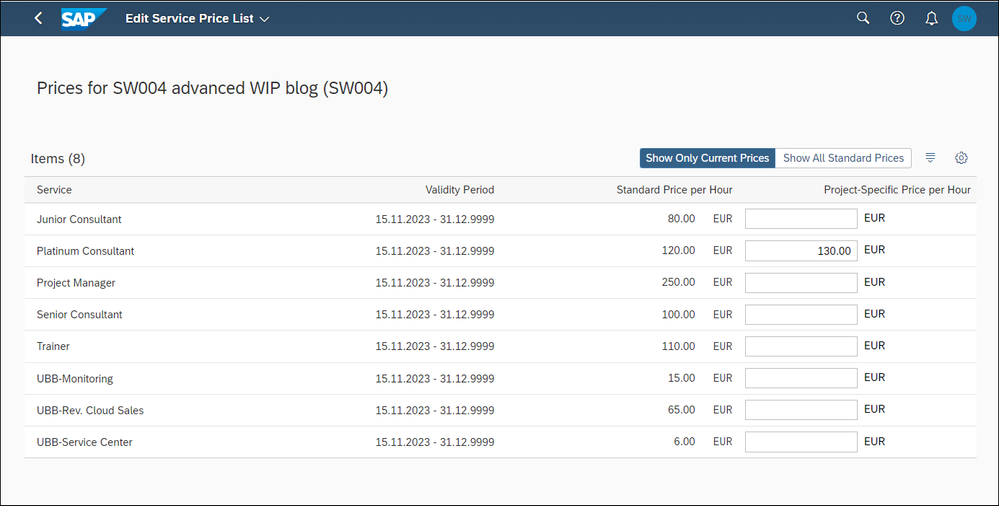
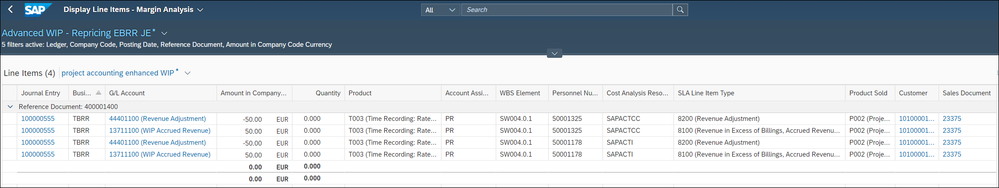
Repricing
During the lifetime of a project the service prices may change generally, or the project manager needs to change the prices project specifically. For this case a job is provided by the project billing application to adjust the billable value of the confirmed, not yet billed hours. Additionally, EBRR is called to adjust the WIP.
The principle and the number of journal entry items are unchanged, but we apply in this method the billed product in the journal entry items.
We first adjust the projects specific prices with the Plan Customer Projects app. Within the billing tab you can access service price List.
Then we start the job for repricing with the Schedule Repricing for Projects app.
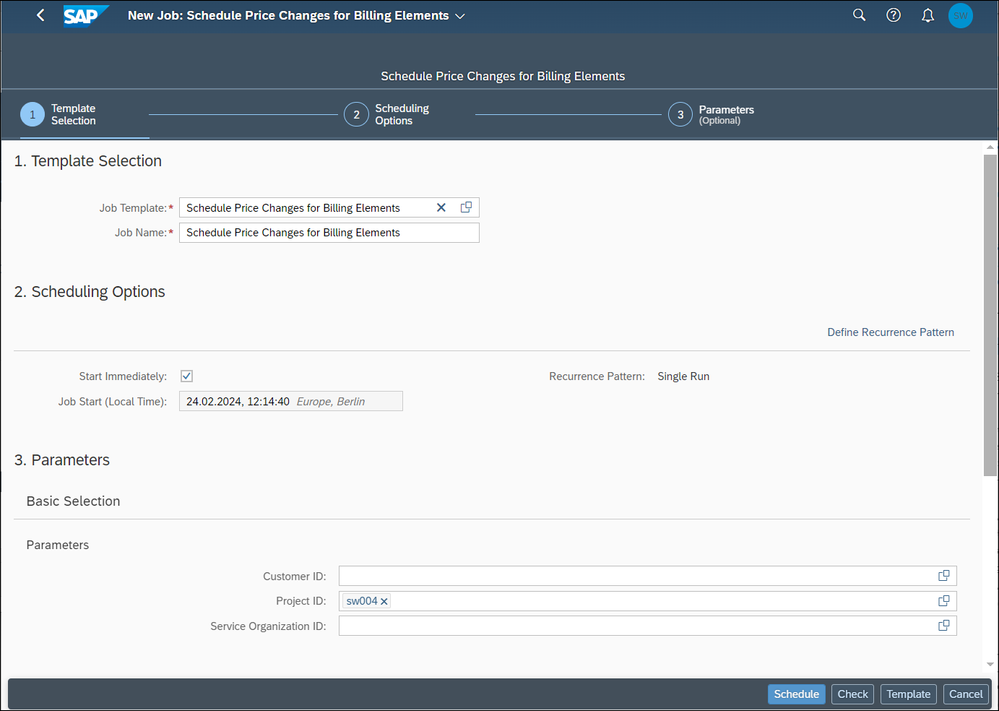
With the job EBRR closing run is triggered in background for the selected projects.
Control in event-based revenue recognition
To utilize the advanced WIP reporting, which we showed above, a new revenue recognition key ‘SPTMWP’ and a new revenue recognition method ‘23’ have been provided with CE2402.
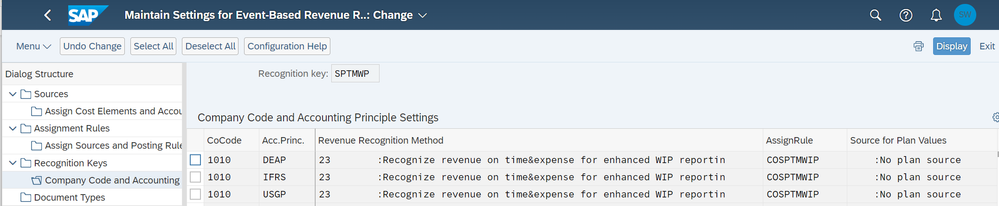
Additionally, a new assignment rule ‘COSPTMWIP ‘has been delivered, which includes the new posting logic for write off and the revenue cap.

Besides the CAP posting logic, there is no difference in the posting logic from the EBRR key SPTM. It is therefore possible to change the key for existing professional service customer projects. In other words, you can switch in professional service customer projects from SPTM to SPTMWP – even if there are already postings with EBRR key SPTM.
EBRR key change for a wbs billing element
We now show the project GH001 that has the EBRR key SPTM assigned and there has already been time confirmations. On the WBS element GH001.1.1 there are already confirmations provided:
- a senior consultant reported 5 hours.
- a platinum consultant 3 hours.
- In addition, one hour has already been written off from the platinum consultant.
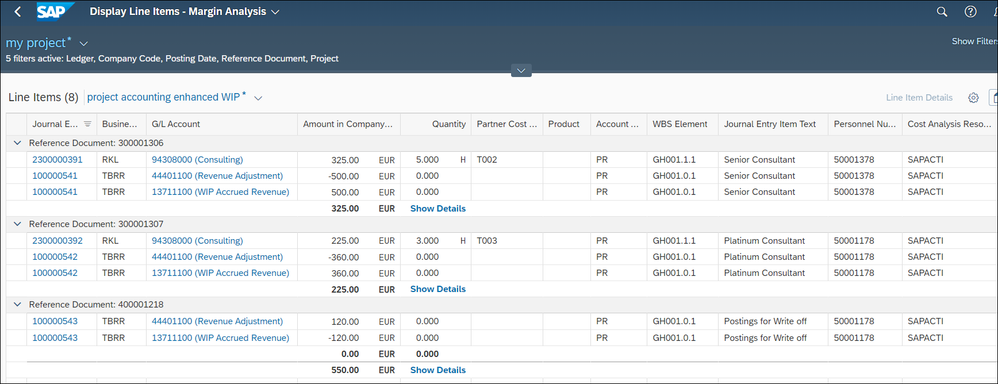
The same behavior in the second time confirmation with reference number 30001307. Here a platinum consultant with the personnel number 50001178 has confirmed 3 hours.
The third posting with reference number 400001218 shows a write off from 1h for the platinum consultant. The hours are also missing here, and beyond that there is no other identifier in the entry by which one could recognize that it is a write off.
To get the new advanced WIP Reporting the Event Based Revenue Recognition key can now be changed. To do this, we use the Event Based Revenue Recognition Monitor for Projects and select the WBS element GH001.01.1.
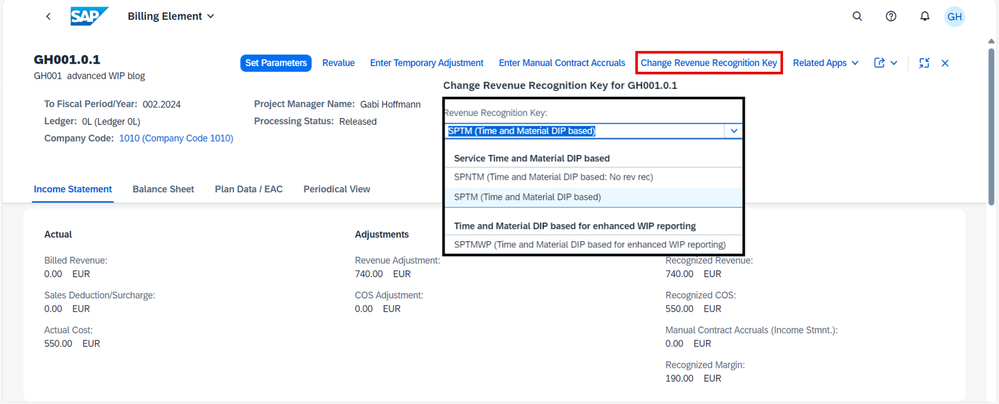
It is important to know that there are rules associated with the dropdown menu. If one of the rules described below applies, the key is displayed in the drop-down list. These rules do not only apply to the change we describe here but are generally valid.
The rules for rev rec key change:
- No postings have been made. You can change the revenue recognition key to any revenue recognition key within the same revenue recognition area.
- In case any posting has already been made:
- You can change the original revenue recognition key to a new revenue recognition key, if the assignment rules are equal.
- You can change the original revenue recognition key to a new revenue recognition key within the same area if the assignment rules are not equal, but the assigned G/L accounts are equal.
Now back to our example. The Event Based Revenue Recognition key has been changed and saved. Next, it is necessary to trigger a EBRR period-end calculation for the WBS element. In the pop up we select Simulate and get the results in figure 24.
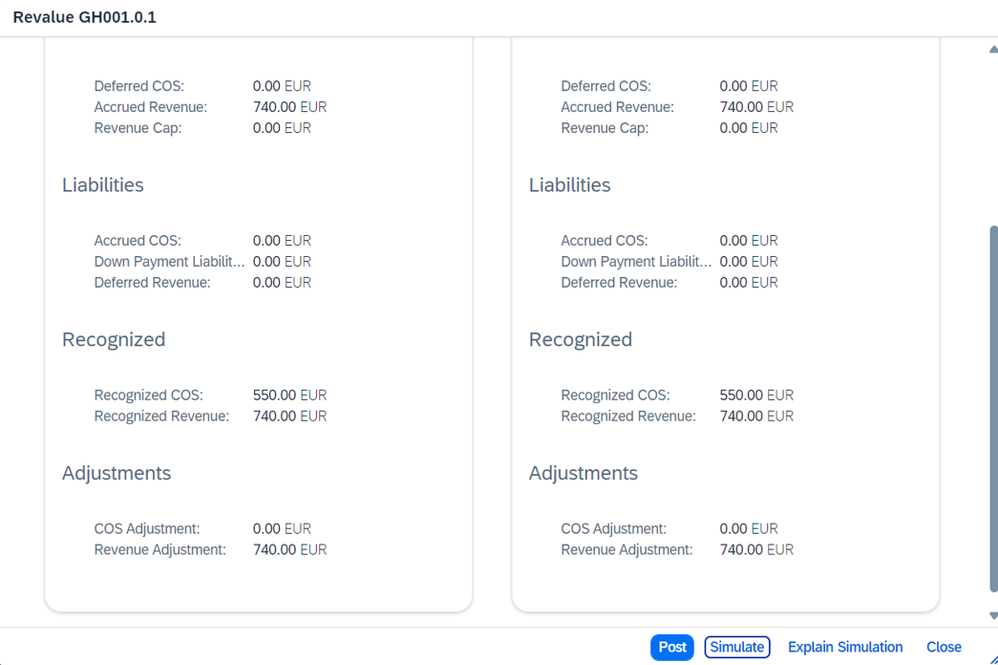
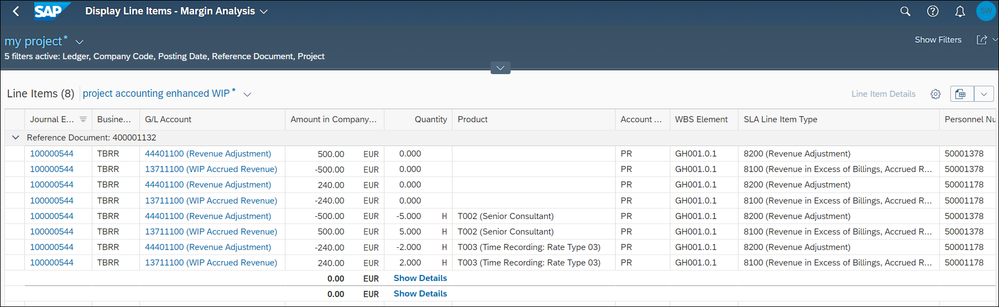
- time confirmation of the senior consultant of 5 hours is cancelled with the first two lines which have a value of 500 €.
- The hours of the Platinum consultant are also cancelled. This can be seen in lines 3 and 4, which have a value of 240 €. Please note that the Platinum consultant has reported 3 hours. However, one hour of these 3 hours has already been written off. At the time of the period-end closing, there are two hours in the WIP for the Platinum consultant that have not been invoiced.
In the next 4 journal entry items the EBRR journal entries are posted again with the new key:
- The senior consultant's hours are posted in lines 5 and 6. For this purpose, the number of open hours and the billed product was previously determined. Both are transferred to the posting. We see 5h in our quantity field and the billed product T002.
- Lines 7 and 8 now contain the 2 hours of the Platinum Consultant with the corresponding billed product T003.
There are no additional posting journal entry items for the write off, the written off hour is considered in the calculation of the WIP. There is no update of the new SLA type for write off. This information cannot be transferred to the new rev rec method. Only write off with active advanced WIP rev rec key updates the new write off information with SLA type.
Closing remarks
We hope you enjoyed these insights in WIP analysis for customer projects in S/4HANA public cloud. It is another scenario, in which we are now benefiting from the innovations in financial accounting.
Feedback welcome
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud for Professional Services,
- FIN Controlling,
- SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
1 -
Business Trends
363 -
Business Trends
24 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT)
1 -
Event Information
461 -
Event Information
24 -
Expert Insights
114 -
Expert Insights
160 -
General
1 -
Governance and Organization
1 -
Introduction
1 -
Life at SAP
415 -
Life at SAP
2 -
Product Updates
4,684 -
Product Updates
220 -
Roadmap and Strategy
1 -
Technology Updates
1,502 -
Technology Updates
89
- Jumpstart your cloud ERP journey with guided enablement in RISE with SAP Methodology in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- SAP S4HANA Cloud Public Edition Logistics FAQ in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Stock Ageing Report just gone live of SAP S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Restriction on number of consolidation units in SAP Group Reporting Public Cloud edition. in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Explanation of the Delta Posting Logic in Advanced Foreign Currency Valuation in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 8 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 |