- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by SAP
- Accruals Management - Purchase Order Accruals and ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
This blog will introduce you to Accruals Management and how it is realized in SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Public Edition including both purchase order accruals and deferrals. And it is intended for business users and consultants, as well as for anyone interested to learn about accruals management.
Business Context
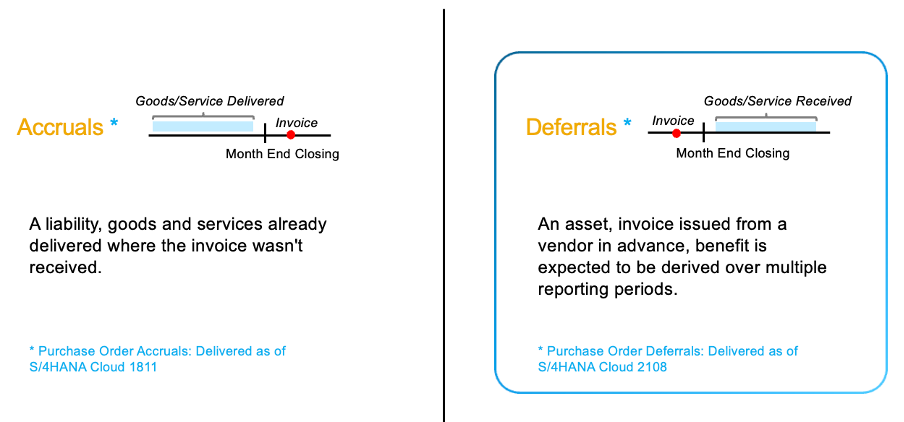
Pic #1: Accrual Management Business Context
Accrual accounting recognizes revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is exchanged. When we talk about Accruals Management in SAP, we are generally referring to the expenses part of accrual accounting, while the revenues part is covered by Revenue Recognition functions.
Accrued Expenses are costs that a business has incurred but hasn't yet paid. For example, if a company receives goods or services from a supplier but hasn't received the invoice by the end of the accounting period, the business would record an accrued expense.
Deferred Expenses (or also called Prepaid Expenses) are payments a business makes for goods or services it will receive in the future. For example, a company might prepay its rent for the year or its insurance premiums.
The financial impact of these two accounting concepts typically appears on the balance sheet (as liabilities for accrued expenses and as assets for deferred expenses) and on the profit and loss statement (as expenses when recognized).
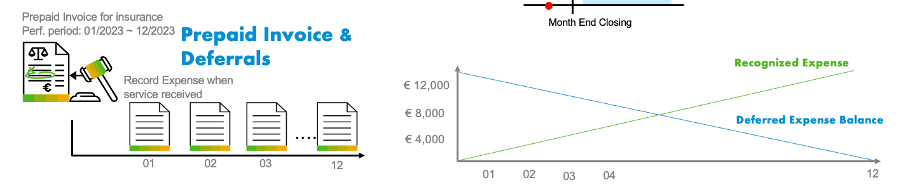
Pic # 2: Deferral Example
Insurance is a typical example of a deferred expense. When a business pays for insurance, it's often paid in advance for a period of time. For example, a company pays 12,000EUR for a year of insurance upfront, classifying this as a deferred expense. Each month, 1,000EUR of this prepaid expense is recognized as an insurance expense on the Profit & Loss Statement.
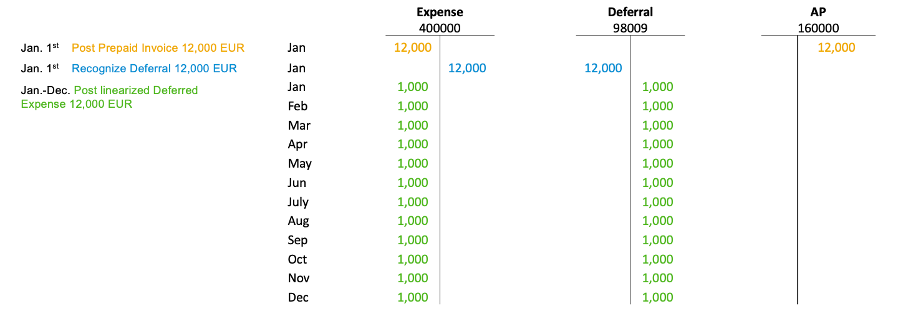
Pic #3: Posting in T-Accounts
Above you can see the posting example in T-Accounts.
Challenges in Traditional Approach
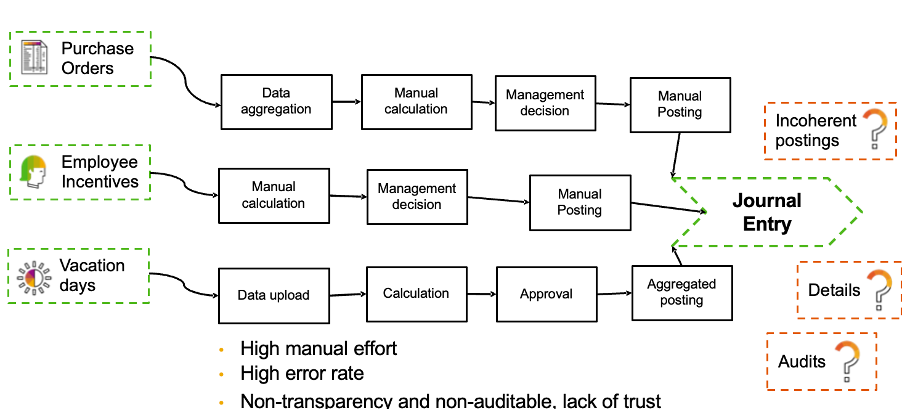
Pic #4: Challenges in Traditional Approach
In the traditional approach of accruals management, customers face business challenges, such as high manual efforts, high error rate and the lack of transparency with regard to how accruals and deferrals are calculated, the status of the process and their influence on overall KPIs as shown in above picture.
The traditional approach of creating recurring journal entries for such invoices shall be replaced by an automated procedure.
Both accruals and deferrals are integral part of Accruals Management. Similar to Purchase Order Accruals, it shall also be possible to calculate and post Purchase Order Deferrals in an automated manner. In some business scenarios accruals and deferrals seamlessly interplay with each other.
SAP Accruals Management Process Overview
5: SAP Accruals Management Process Overview
SAP Accruals Management is designed to support customers along the entire process of accruals and deferrals, from collecting inputs, calculating the correct amounts, allowing accountants or stakeholders to review the proposed amounts and posting of the journal entries. It helps to automate the process with a reliable outcome.
Purchase Order Deferrals’ Solution Overview
Pic #6: Purchase Order Deferrals’ Solution Overview
The accrual objects are automatically created from the purchase order data with the unified structure, then based on these data SAP S/4HANA Accrual Engine will propose how to calculate and post the accruals and deferrals. Throughout the entire process, accountants work in a unified environment, and embedded analytics give them the full transparency and auditability.
Use Cases in Purchase Order Accruals and Deferrals
Pic #7: use Cases in Purchase Order Accruals and Deferrals
In this comprehensive table you can find all supported use cases and calculation methods that are offered with Purchase Order Accruals and Deferrals. The basic calculation logic for Purchase Order Accruals and Deferrals are as below:
Accruals = Planned Costs – Recognized Costs (only positive value, if negative then ‘0’)
Deferrals = Actual Costs – Recognized Costs (only positive value, if negative then ‘0’)
The Planned Costs, Actual Costs and Recognized Costs are retrieved by system differently basing on different procurement use cases. The use cases are grouped into 2 big categories: Consumable Goods Purchasing and Service Purchasing. There are 3 further cases under Consumable Goods Purchasing and 2 further cases under Service Purchasing. Please kindly refer to the above table for the detailed calculation of costs.
Demo
Please refer to the below SAP Microlearning for a system demo about how accruals and deferrals are posted in SAP S/4HANA Cloud system.
Pic #8: SAP Microlearning
Additional Information
Help Documentation
Demos and Videos
- Demo Store: Purchase Order Accruals & Service Entry Sheet Accruals
- Demo Store: Purchase Order Deferrals
Blogs
- Post Accruals/Deferrals in a Smart Way | SAP Blogs
- Purchase Order Accruals – Scope item 2VB | SAP Blogs
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud,
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud for Finance
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
1 -
Business Trends
363 -
Business Trends
24 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT)
1 -
Event Information
461 -
Event Information
24 -
Expert Insights
114 -
Expert Insights
160 -
General
1 -
Governance and Organization
1 -
Introduction
1 -
Life at SAP
415 -
Life at SAP
2 -
Product Updates
4,684 -
Product Updates
220 -
Roadmap and Strategy
1 -
Technology Updates
1,502 -
Technology Updates
89
- Rebate Accruals validity period issue in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Purchase Order Accrual in S/4HANA - Part 2 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- Purchase Ordre Accrual in S/4HANA - Part 1 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- ACM capabilities in a nutshell - Contracting Part 2 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 9 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 |